고막 통기관 삽입 치료와 중이염, Eardrum ventilation intubation treatments for otitis media
- 잘 낫지 않는 삼출성 중이염(장액성 중이염)을 약물이나 다른 방법으로 적절히 치료해도 잘 낫지 않거나
- 중이 강 속과 이관 입구의 사이에 있는 이관에 이관염이 있거나 다른 어떤 병변이 있어 인두와 중이 강 속 공기가 정상적으로 잘 유통되지 않을 때 이관 기능 장애가 있어 중이 강 속과 이관 입구 사이에 있는 이관을 통해 공기가 유통되지 않을 때 작은 튜브(그림 75,76,77 참조)를 고막에 끼어 외이도 내와 중이 강 내에 공기가 잘 유통하게 하는 치료를 고막 통기관 삽입 치료라고 한다.
- 이 수술은 전신마취 하에서 하는 소아 외과적 수술치료 중 최근 가장 많이 하는 수술 중 하나이다.
사진 75. 치료가 잘 되지 않는 삼출성 중이염은 통기관 고막 삽입으로 치료할 수 있다. 외이도 내 공기와 중이강 내 공기가 고막 통기관을 통해 잘 유통되면 삼출성 중이염이 잘 치료될 수 있다. (이미 장치했던 통기관의 사진. 그래서 좀 지저분해보인다.)
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP

사진 76. 잘 치료되지 않는 삼출성 중이염을 치료할 때 쓸 수 있는 고막 통기관의 일종.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP

사진 77. 잘 치료되지 않는 삼출성 중이염을 치료할 때 쓸 수 있는 고막 통기관의 일종.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP

사진 78. 고막에 꽂은 통기관을 통해 중이강 내에서 고름(이루)이 외이도 내로 흘러나온다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
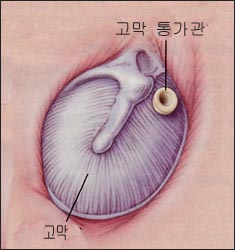
그림 79.그림으로 본 고막에 삽입된 통기관과 고막.
출처: N Eng J. Med, Vol.344, No.!6. April 19, 2001. p1177
어떤 경우, 고막 통기관 삽입 치료를 권장하나
① 삼출성 중이염이 3개월 이상 지속될 때 특히 청력이 감소되거나 중이가 충혈 되어 있을 때
② 급성 중이
염이 3번 이상 재발되고 적어도 최근에 한 번 재발됐을 때
③ 재발된 급성 중이염을 항생제로 예방적 치료를 하는 동안 급성 중이염이 2번 이상 생겼을 때
④ 6개월 동안 급성 중이염이 4번 이상 생기거나 12개월 동안에 급성 중이염이 6번 이상 생길 때
⑤ 화농성 유양돌기 염을 치료할 때
⑥ 이관 기능 부전증과 중이 무기증이나 고막함몰이 지속될 때
고막 통기관 삽입 치료로 인한 합병증
① 고막 통기관 삽입 치료를 하기 위해 삽입된 통기관이 있어야 할 제자리에 있지 않고 다른 부위로 탈출될 수 있다.
② 안면신경이 손상될 수 있다.
③ 중이 강 내 이소골이 손상될 수 있고
④ 이관 기능부전증이 있을 때 고막 통기관 삽입 치료를 여러 번 해야 할 때도 있다.
⑤ 고막 통기관 삽입 치료를 한 고막의 26~50%에서 고막상흔이나 고막위축이 생길 수 있다.
⑥ 전신마취로 인한 합병증이 생길 수 있으나 아주 드물게 생긴다.
⑦ 고막 통기관 삽입 장치를 한 후 5~14%에서 고막에 육아종이 형성될 수 있다.
⑧ 고막 통기관 삽입을 한 후 만성 중이염이 생길 수 있고 중이강 내에서 이루가 계속 날 수 있다. 이루를 Oflocin(Ffloxin otic solution)으로 치료할 수 있다. Ciprofloxacin/dexamethasone 등 귀 점적약제로 치료하면 치료효과가 좋다(출처-Pediatric News, March 2004).
⑨ 고막 통기관 삽입 치료를 한 후 고막과 중이강 내에서 피고름이 날 수 있다.
⑩ 삽입한 고막 통기관을 전신마취 하에 빼야 할 때도 있다.
⑪ 콜레스테린종(진주종)이 형성 될 수 있다.
⑫ 4~25% 정도 고막천공이 생길 수 있다.
고막 통기관 삽입치료를 시작 한 후 얼마 후에 자연적으로 빠질 수 있나
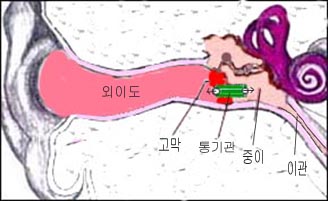
그림 81. 고막 통기관 삽입 치료.
a-고막, b-통기관, c-중이강.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
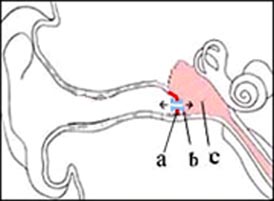
그림 80. 고막 통기관 삽입 치료.
a-고막, b-통기관, c-중이강. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
- 고막 통기관 삽입을 한 후 10개월에 자연히 빠져나오는 확률이 50%이다.
Eardrum ventilation intubation treatments for otitis media
• Otitis media with effusion that does not heal well (serous otitis media) does not get better even with adequate treatment with drugs or other methods, or
• When the air in the pharynx and middle ear cavity does not flow normally due to otitis or any other lesion in the ear canal between the middle ear cavity and the entrance to the ear canal When air is not circulated through the tympanic membrane, a small tube (refer to Figs. 75, 76, 77) is inserted into the eardrum to allow good air circulation in the ear canal and the middle ear cavity. This is called tympanic ventilation tube insertion therapy.
• This operation is one of the most frequently performed pediatric surgical treatments under general anesthesia.

Photo 75. Otitis media with effusion that does not treat well can be treated with ventricular tympanic membrane insertion. Otitis media with effusion can be treated well if the air in the external auditory meatus and in the middle ear cavity are well circulated through the tympanic cavity. (Photo of the vent pipe I already installed. So it looks a little messy.) Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP

Photo 76. A type of tympanic ventilator that can be used to treat poorly treated otitis media with effusion. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP

Photo 77. A type of tympanic ventilation tube that can be used to treat poorly treated otitis media with effusion. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP

Photo 78. Pus (fissure) flows out from the middle ear cavity into the ear canal through the ventilation tube inserted into the eardrum. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP

Figure 79. Ventilation tube and tympanic membrane inserted into the tympanic membrane as seen in the diagram. Source: N Eng J. Med, Vol.344, No.!6. April 19, 2001. p1177 In some cases, tympanic ventilation is recommended
① When otitis media with effusion lasts for more than 3 months, especially when hearing is reduced or the middle ear is congested
② Acute middle ear 3 or more recurrences of inflammation and at least one recent recurrence
③ When acute otitis media occurs twice or more during prophylactic treatment of recurrent acute otitis media with antibiotics
④ When acute otitis media occurs 4 or more times in 6 months or acute otitis media occurs 6 or more times in 12 months
⑤ When treating purulent mastoiditis ⑥ When ear tube insufficiency and middle ear atelectasis or tympanic depression persist
Complications from tympanic tube insertion therapy
① For the tympanic ventilation tube insertion treatment, the inserted ventilation tube may not be in the place it should be and may prolapse to another area.
② The facial nerve may be damaged.
③ The ossicles in the middle ear cavity may be damaged ④ When there is ETD, it is sometimes necessary to insert the tympanic tube several times
⑤ Eardrum scars or atrophy of the eardrum may occur in 26-50% of eardrums treated with a tympanic tube insertion treatment.
⑥ Complications may occur due to general anesthesia, but they occur very rarely.
⑦ Granulomas may form in the tympanic membrane in 5 to 14% of cases after the tympanic tube insertion device.
⑧ After the tympanic tube is inserted, chronic otitis media may occur and the ear canal may continue to appear in the middle ear cavity. Ears can be treated with Oflocin (Floxin otic solution). Treatment with ear drops such as Ciprofloxacin/dexamethasone is effective (source-Pediatric News, March 2004).
⑨ After the tympanic tube insertion treatment, blood pus may appear in the tympanic membrane and the middle ear cavity. ⑩ There are times when the inserted tympanic tube must be removed under general anesthesia.
⑪ Cholesterinoma (Pearloma) may be formed.
⑫ Perforation of the tympanic membrane may occur in 4-25% of cases. How soon after tympanic tube insertion treatment begins, can it fall out naturally?

Figure 81. Typhoid ventilator implantation treatment. a – tympanic membrane, b – ventilator, c – middle ear cavity. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP

Figure 80. The treatment of tympanic duct insertion. a – tympanic membrane, b – ventilator, c – middle ear cavity. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
• There is a 50% chance that the tympanic tube will come out spontaneously at 10 months after insertion.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy of Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제1권 소아청소년 응급 의료
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제2권 소아청소년 예방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제3권 소아청소년 성장 발육 육아
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제4권 모유,모유수유, 이유
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유식, 비타민, 미네랄, 단백질, 탄수화물, 지방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제16권. 소아청소년 정형외과 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제17권. 소아청소년 피부 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제18권. 소아청소년 이비인후(귀 코 인두 후두) 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제19권. 소아청소년 안과 (눈)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제20권 소아청소년 이 (치아)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제21권 소아청소년 가정 학교 간호
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제22권 아들 딸 이렇게 사랑해 키우세요
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제23권 사춘기 아이들의 성장 발육 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제24권 소아청소년 성교육
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제25권 임신, 분만, 출산, 신생아 돌보기
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th- 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
- 응급환자관리 정담미디어
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- 소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
- The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
- Neonatology Jeffrey J. Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
- Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- 임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
- Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
- Sources and references on Growth, Development, Cares, and Diseases of Newborn Infants
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
- Emergency care, Harvey Grant and Robert Murray
- Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
- Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
- Neonatal resuscitation Ameican academy of pediatrics
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A.
- 제4권 모유, 모유수유, 이유 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유, 비타민, 단백질, 지방 탄수 화물 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제6권 신생아 성장발육 양호 질병 참조문헌 및 출처
- 소아과학 대한교과서
-
제18권 소아청소년 이비인후과 질환 참조문헌 및 출처
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Gray’s Anatomy
-
Habilitation of The handicapped Child, The Pediatric Clinics of North America, Robert H Haslam, MD.,
-
Pediatric Otolaryngology Sylvan Stool
-
Hearing Loss In children, The Pediatric Clinics of North America Nancy Roizen,MD and Allan O Diefendorf, PhD
-
Recent Advances in Pediatric otolaryngology The Pediatric Clinics of North America
-
Pediatric Otolaryngology. The Pediatric Clinics of North America, David Tunkel, MD., Kenneth MD Grundfast, MD
Copyright ⓒ 2014 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
“Parental education is the best medicine.