신생아 안면신경 마비, Facial nerve palsy in newborn infants
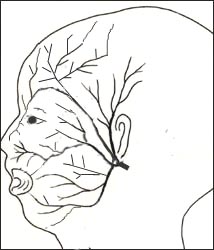
그림 195. 안면신경 분포도
안면신경은 12쌍의 뇌신경 중 제7번째 뇌신경이다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
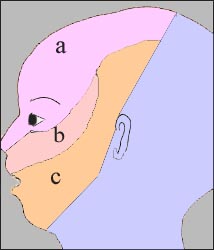
그림 196. 안면신경 분포도
주 안면신경은 6개의 분지로 나누어져 얼굴 이마 눈, 혀 등에 분된다.
a-안면신경의 눈 부분, b-안면신경의 상악 부분, c-안면신경의 하악 부분
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
- 정상적으로 모두 12쌍의 뇌신경들이 있다.
- 12쌍의 뇌신경들은 두개강 속에 있는 뇌에서 기시되어 두개골에 뚫려 있는 각 뇌신경 구멍을 통과한 후 두개강 밖으로 나온 후 머리·눈·코·입·위·얼굴·입·인두·심장·위장 등에 분포된다.
- 12쌍 뇌신경들 중 안면신경은 제7 뇌신경이다.
- 안면신경은 좌우 얼굴에 퍼져 있다.
- 좌우 얼굴에 있는 한쪽 안면신경은 그 쪽 얼굴 등에만 국한되어 분포된다.
- 신생아에게도 안면 신경 마비가 올 수 있고 신생아기 이후 아이들에게도 안면 신경마비가 생길 수 있다.
신생아의 안면신경 마비의 원인
① 어려운 분만으로 태어난 신생아
② 태아의 얼굴이 엄마의 산도에 정상 이상으로 눌릴 때
③ 겸자 분만으로 태어날 때 태아의 얼굴이나 머리가 겸자로 눌릴 때
④ 뇌 속에 있는 안면신경 기시부 무발육이 선천성으로 생길 때
⑤ 선천성 하악골 무 발육과 함께 생길 수 있다.
⑥ 쌍태 임신 중 한 태아의 얼굴이 다른 태아의 얼굴 등으로 오랫동안 눌리고 그로 인해 안면신경이 눌릴 때 한쪽이나 좌우 양쪽 안면신경이 마비될 수 있다.
⑦ 두개골에 있는 안면신경 구멍을 통과해서 한 쪽 안면신경 원줄기가
-
- 눈 부분 가지,
- 상악 부분 가지,
- 하악 부분 가지로 나누어지는 것이 정상이다.
- 그 중 한 쪽 안면신경 원줄기가 다 마비될 수도 있고 안면신경가지 중 한 가지만 마비될 수도 있다.
⑧ 드물게 분만과는 관련 없이 안면신경이 시작되는 두개강 내 뇌 부위가 손상되어 그 쪽 안면신경 줄기가 다 마비될 수 있다.
⑨ 신생아기 이후의 아이의 한 쪽 안면신경의 전체가 확실한 원인이 없이 갑자기 마비될 수 있다.[부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다-소아가정간호백과]-제 12권 소아청소년 신경 정신 행동, 수면문제-안면신경 마비 참조
신생아의 안면신경 마비의 증상 징후
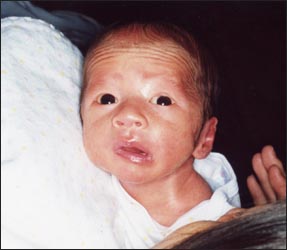
사진 197. 쌍태아 신생아의 좌 안면신경 마비
태어나기 전 자궁 내에서 다른 쌍 태아에게 눌려서 생긴 말초 안면신경마비로 진단 받고 생후 2개월 내 관찰 치료를 받은 후 자연 회복됐다.아무런 치료를 하지 않고 자연히 회복됐다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
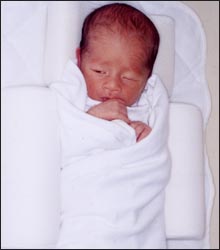
사진 198. 쌍태아 신생아의 좌 안면신경 마비
태어나기 전 자궁 내에서 다른 쌍태아에게 눌려 생긴 말초 안면신경마비로 진단 받고 생후 2개월 내 자연 회복됐다. 안면신경 마비로 좌측 눈을 완전히 들 수 없다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
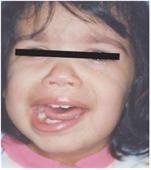
사진1-217. 3세 유아의 좌측 안면신경의 말초부분이 라임 병으로 마비됐다.
▴ Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
- 손상된 안면신경의 부위에 따라, 안면신경 손상의 정도, 원인에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다. 선천성으로 생긴 선천성 안면신경 마비와 후천성으로 생긴 후천성 안면신경 마비의 증상 징후가 다르다.
- 안면신경의 6개 분지들 중 한 분지만 손상될 때는 그 분지에 의해 분포된 얼굴 부위에만 안면신경의 마비가 일부 생길 수 있다.
- 또한 안면신경이 시작되는 뇌 기시 부위가 손상되어 그쪽 안면신경이 전부 마비될 때와 두개골의 밖으로 나와 있는 안면신경의 여러 분지들 중 한 가지만 마비될 때의 증상 징후가 각각 다르다.
- 안면신경이 시작되는 뇌 기시 부위에 있는 안면신경이 손상될 때는 손상된 부위의 반대 쪽에 있는 얼굴 반쪽이나 ⅔ 정도가 전 얼굴이 마비될 수 있다.
- 안면신경이 뇌 기시부에서 나와 두개골의 밖으로 나온 후 그쪽 안면신경의 전부가 마비되면 마비된 안면신경이 분포된 쪽 입을 크게 벌리고 다물 수 없다.
- 울 때도 마비된 쪽의 입을 잘 벌릴 수 없다.
- 마비된 쪽 코와 입술 사이에 있는 피부 주름살(비순 주름살)이 약하게 얇게 잡힌다.
- 마비되지 않은 안면신경이 있는 쪽 입(사진 197 참조)은 힘 있게 벌리고 다물 수 있으며, 비순 주름살은 깊고 힘 있게 잡혀서 입 전체가 비뚤어진다.
- 마비된 쪽 눈을 꼭 감을 수가 없다(사진 198 참조).
- 그쪽 눈에서 눈물이 나오지 않을 수 있다.
- 마비된 쪽 얼굴을 찌푸릴 때 비순의 주름살이 작게 생기고 그쪽 얼굴 전체에 힘이 약하다.
- 마비된 쪽 이마에 생긴 주름살이 없어질 수 있다.
- 선천성으로 한쪽 안면신경의 여러 분지들 중 한두 개의 분지가 마비될 때는 그에 따라 안면 근육들 중 한두 개의 근육에만 마비가 올 수 있다.
- 마비된 쪽 구각(口角)이나 아랫입술이 정상 쪽 아랫입술보다 더 미약할 수 있다.
- 이런 경우는 보기에 그리 나쁘지 않다.
신생아의 안면신경 마비의 진단
- 병력·증상 징후·진찰소견 등을 종합해서 진단할 수 있다.
- 신생아기 이후 아이들에게 오는 안면신경 마비는 라임병 등으로 생길 수 있다.
- 따라서 그런 병을 감별 진단해야 한다.
신생아의 안면신경 마비의 치료
- 안면신경 마비가 안면신경의 뇌 기시부에서 얼굴에 분포되기까지의 어느 부분에 손상이 생겼는지,
- 어떤 형의 안면신경 마비인지,
- 안면신경 마비의 원인에 따라 치료가 다르다.
- 대부분의 안면신경의 말단 분지가 마비됐을 때는 1∼2주 이내 저절로 회복되는 경우가 많다.
- 아무런 치료가 필요치 않을 때가 많다.
- 안면신경이 마비된 쪽 눈에서 눈물이 나지 않고 그 눈을 정상적으로 감을 수도 없고 각막이 건조돼서 각막 손상이 생길 수 있다.
- 이 경우, 안과 전문의 처방에 따라 인공눈물을 눈에 넣어 치료 한다.
- 원인에 따라 수술로 치료하기도 하고,
- 또 영구적으로 회복되지 않을 수도 있다.
Facial nerve palsy in newborn infants

Figure 195. Facial Innervation Map The facial nerve is the 7th cranial nerve out of 12 pairs of cranial nerves. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP

Figure 196. Facial Innervation Map The main facial nerve is divided into 6 branches and is divided into the face, forehead, eyes, and tongue. a – the eye part of the facial nerve, b – the maxillary part of the facial nerve, c – the mandibular part of the facial nerve Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
• Normally there are 12 pairs of cranial nerves in all.
• Twelve pairs of cranial nerves originate from the brain in the cranial cavity, pass through each cranial nerve hole in the skull, and then come out of the cranial cavity and are distributed to the head, eyes, nose, mouth, stomach, face, mouth, pharynx, heart, stomach, etc..
• Of the 12 pairs of cranial nerves, the facial nerve is the 7th cranial nerve.
• Facial nerves spread to the left and right faces.
• One facial nerve in the left and right faces is distributed limitedly to the face, etc. on that side.
• Facial nerve palsy can occur in newborns, and facial nerve palsy can also occur in children after the neonatal period.
Causes of facial nerve palsy in newborns
① Newborns born through a difficult delivery
② When the face of the fetus is pressed by the mother’s birth canal more than normal
③ When the baby is born by forceps delivery When the face or head of the fetus is pressed with forceps
④ When facial nerve origin in the brain is congenital
⑤ It can occur together with congenital mandibular insufficiency.
⑥ During twin pregnancy, when the face of one fetus is pressed by the face of the other fetus for a long time and the facial nerve is pressed for a long time, one or both left and right facial nerves may be paralyzed.
⑦ One facial nerve main stem passes through the facial nerve hole in the skull
o eye branches,
o maxillary branch,
o Mandibular division is normal.
o One of the facial nerve main stems may be paralyzed, or only one of the facial nerve branches may be paralyzed.
⑧ Rarely, the part of the brain in the cranial cavity, where the facial nerve begins, is damaged unrelated to childbirth, and the entire facial nerve stem may be paralyzed.
⑨ The entire facial nerve of one side of a child after neonatal period may be suddenly paralyzed without a definite cause.
See Facial Nerve Paralysis
Signs of symptoms of facial nerve palsy in newborns

Photo 197. Left facial nerve palsy in twin newborns He was diagnosed with peripheral facial nerve palsy, which was caused by pressure from another twin in the womb before birth, and recovered naturally after receiving observational treatment within 2 months of age. He recovered naturally without any treatment. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP

Photo 198. Left facial nerve palsy in twin newborns He was diagnosed with peripheral facial nerve palsy, which was caused by pressure from another twin in the womb before birth, and recovered spontaneously within 2 months of age. The left eye cannot be fully lifted due to facial nerve palsy. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP

Picture 1-217. The peripheral part of the left facial nerve of a 3-year-old infant was paralyzed due to Lyme disease.
▴ Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
• Symptoms and signs differ depending on the area of the damaged facial nerve, the degree of facial nerve damage, and the cause.
The symptoms and signs of congenital facial nerve palsy and acquired facial nerve palsy are different.
• When only one branch of the six branches of the facial nerve is damaged, partial paralysis of the facial nerve may occur only in the facial area distributed by that branch.
• Also, when the facial nerve originating from the brain is damaged and the facial nerve is completely paralyzed, symptoms are different when only one of the branches of the facial nerve outside the skull is paralyzed.
• When the facial nerve is damaged in the brain origin where the facial nerve begins, half or half of the face on the opposite side of the damaged area may be paralyzed.
• After the facial nerve comes out of the brain’s origin and comes out of the skull, if all of the facial nerve is paralyzed, it is impossible to open and close the mouth on the side where the paralyzed facial nerve is distributed.
• Difficulty opening the mouth on the paralyzed side even when crying.
• The skin folds (nasolabial folds) between the nose and lips on the paralyzed side are slightly thinned out.
• The mouth on the side with the unparalyzed facial nerve (see photo 197) can be opened and closed with power, and the nasolabial folds are deeply and powerfully gripped so that the entire mouth is crooked.
• Inability to close the eye on the paralyzed side (see photo 198).
• Tears may not come out of that eye.
• When you frown on the paralyzed side, small wrinkles appear on the cheekbones, and the strength of the entire face is weak.
• Wrinkles on the forehead on the paralyzed side may disappear.
• When one or two branches of the facial nerve are congenitally paralyzed, only one or two of the facial muscles may be paralyzed accordingly.
• The paralyzed corner of the mouth or lower lip may be weaker than the normal lower lip.
• This case doesn’t look too bad.
Diagnosis of facial nerve palsy in newborns
• Diagnosis can be made by combining medical history, symptoms, signs, and examination findings.
• Facial nerve palsy in children after neonatal period can be caused by Lyme disease, etc.
• Therefore, such a disease should be differentially diagnosed.
Treatment of facial nerve palsy in newborns
• What part of the facial nerve palsy from the brain origin of the facial nerve to distribution to the face is damaged;
• What type of facial nerve palsy is,
• Treatment differs depending on the cause of facial nerve palsy.
• When most of the terminal branches of the facial nerve are paralyzed, they often recover spontaneously within 1 to 2 weeks.
• Often no treatment is needed.
• In the eye where the facial nerve is paralyzed, tears do not flow, the eye cannot close normally, and the cornea becomes dry, which can cause corneal damage.
• In this case, according to the prescription of an ophthalmologist, artificial tears are put into the eyes for treatment.
• Depending on the cause, it may be treated with surgery,
• You may not recover permanently.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy of Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제1권 소아청소년 응급 의료
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제2권 소아청소년 예방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제3권 소아청소년 성장 발육 육아
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제4권 모유,모유수유, 이유
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유식, 비타민, 미네랄, 단백질, 탄수화물, 지방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제16권. 소아청소년 정형외과 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제17권. 소아청소년 피부 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제18권. 소아청소년 이비인후(귀 코 인두 후두) 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제19권. 소아청소년 안과 (눈)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제20권 소아청소년 이 (치아)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제21권 소아청소년 가정 학교 간호
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제22권 아들 딸 이렇게 사랑해 키우세요
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제23권 사춘기 아이들의 성장 발육 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제24권 소아청소년 성교육
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제25권 임신, 분만, 출산, 신생아 돌보기
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th- 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
- 응급환자관리 정담미디어
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- 소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
- The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
- Neonatology Jeffrey J. Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
- Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- 임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
- Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
- Sources and references on Growth, Development, Cares, and Diseases of Newborn Infants
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
- Emergency care, Harvey Grant and Robert Murray
- Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
- Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
- Neonatal resuscitation Ameican academy of pediatrics
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A.
- 제4권 모유, 모유수유, 이유 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유, 비타민, 단백질, 지방 탄수 화물 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제6권 신생아 성장발육 양호 질병 참조문헌 및 출처
- 소아과학 대한교과서
-
제18권 소아청소년 이비인후과 질환 참조문헌 및 출처
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Gray’s Anatomy
-
Habilitation of The handicapped Child, The Pediatric Clinics of North America, Robert H Haslam, MD.,
-
Pediatric Otolaryngology Sylvan Stool
-
Hearing Loss In children, The Pediatric Clinics of North America Nancy Roizen,MD and Allan O Diefendorf, PhD
-
Recent Advances in Pediatric otolaryngology The Pediatric Clinics of North America
-
Pediatric Otolaryngology. The Pediatric Clinics of North America, David Tunkel, MD., Kenneth MD Grundfast, MD
Copyright ⓒ 2014 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
“Parental education is the best medicine.