알레르기 비염의 백문 백답, One hundred Qs & As on allergy rhinitis
Q.
알레르기 비염은 유전병입니까
A.
그렇습니다.
대를 이어 체염색체 우성으로 유전됩니다.
이 병은 한 집안의 할아버지 아버지 아들 딸 모두에게 유발될 수 있습니다.
Q.
알레르기 비염은 흔한 병입니까.
A.
미국 전 연령층 사람들의 15∼22%가 알레르기 비염으로 고생하고 있습니다.
또 다른 연구에 의하면, 8.8~16%의 미국 사람들이 알레르기 비염을 앓고 있습니다.
다른 연구에 의하면, 20~30%의 소아청소년들이 알레르기 비염으로 고생하고 있습니다.
그 발병률은 증가 추세에 있습니다.
사춘기 이전 미국 소아들의 10%,
미국 사춘기 아이들과 젊은이들의 20%가 알레르기 비염을 앓고 있습니다.
13,579명의 미국 0-17세 연령층에 속하는 소아청소년들을 대상으로 조사한 결과에 의하면 알레르기 비염의 발병률은 0~4세 연령층에서 4.8%,
5~11세 연령층에서 10.5%,
12~17세 연령층에서 14.2% 이었습니다.
소아청소년들 100명 중 약 10~20명이 알레르기 비염을 앓고 있다고 생각할 수 있습니다.
호흡계의 만성 질환 중 가장 흔한 질환이 알레르기 비염입니다.
그림으로 본 항원
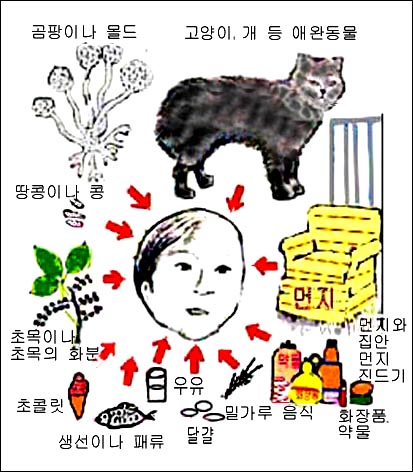
그림 3. 알레르기 질환을 유발시킬 수 있는 항원
개, 고양이 등 애완동물의 털, 비듬, 집 먼지 진드기(집 먼지 좀 진드기),곰팡이,몰드,화분,약물,생선이나 어패류,우유와 우유 음식물,달걀,밀가루 음식물화장품,초콜릿,견과류,땅콩,콩 등
알레르기를 비교적 더 흔히 유발시킬 수 있는 항원들이다.
심한 알레르기 비염이 있는 아이들에게 아데노이드 얼굴형(알레르기 안모)이 생길 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
사진으로 본 항원-Ⅱ

사진 4. 음식물 알레르기를 더 잘 유발시킬 수 있는 음식물
음식물 알레르기를 가장 흔히 일으킬 수 있는 음식물은 달걀, 우유, 메주 콩, 생선과 패류, 땅콩, 호도, 밀가루 등의 음식물이다.
Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

사진 5. 사진에서 보는 음식물로 인해 각종 알레르기 질환이 유발되기 쉽다. 우유, 우유 음식물, 생선, 밀, 조개 등 어패류, 달걀, 땅콩, 호두 등 견과류 등의 음식물은 비교적 더 흔히 알레르기를 유발시킬 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

사진 6. 집 먼지, 집안 먼지 진드기로 알레르기성 비염, 기관지 천식, 아토피성 피부염 등 알레르기성 질환이 유발되기 쉽다.
Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP Q.
알레르기 비염의 원인은 무엇입니까?
A.
이미 말씀드린바와 같이 알레르기 비염에 걸릴 수 있는 체염색체 우성으로 유전되는 유전인자를 소지하고 태어납니다.
거기다가 알레르기를 일으킬 수 있는 항원이 코를 통해서, 경구, 위장관 점막층을 통해서, 피부나 점막층을 통해서, 신체의 다른 계통의 다른 기관을 통해서 신체 내로 들어와서 항원 항체 이상작용이 비강 점막층에서 생깁니다.
그때 비만세포에서 히스타민 과립이 방출되고 그 외 다른 생화학 물질이 복합적으로 작용해서 알레르기 비염이 유발됩니다.
Q.
알레르기 비염 을 일으키는 항원 역할을 하는 것들은 어떤 것이 있나요?
A.
숨 쉴 때 비강을 통해서 기도 속으로 흡입된 초목의 꽃가루, 곰팡이, 몰드, 개, 고양이, 소, 말, 닭, 새 등의 털이나 비듬, 깃털, 침, 죽은 곤충 가루, 집 먼지 좀 진드기, 집 먼지 등이 알레르기 비염을 유발시킬 수 있습니다.
경구와 위장관을 통해 섭취된 우유, 달걀, 초콜릿, 밀가루 음식, 콩, 생선, 땅콩 등의 항원이 피 속으로 들어간 후 비강의 점막층에 도달해서 알레르기 비염을 일으킬 수 있습니다.
피부나 각 기관의 점막층 등을 통해 신체 내로 들어온 항원이 알레르기 비염을 일으킬 수 있습니다.
고양이의 털, 비듬, 또는 침 등이 비강 속으로 직접 흡입될 때 알레르기 비염이 비강 내 점막층에 생길 수 있습니다.
비강 점막층이 고양이 털이나 비듬, 또는 침에 더 이상 접촉되지 않으면 고양이의 털, 비듬, 또는 침 등으로 알레르기 비염이 더 이상 생기지 않는 것이 보통이다.
비강 점막층이 고양이의 털, 침, 비듬 등에 또다시 접촉될 때 고양이 털 항원으로 알레르기 비염이 또다시 생길 수 있다.
Q.
알레르기 비염이 유발되는 기전은 ?
A.
알레르기 비염을 유발시킬 수 있는 항원이 비강 점막층에 도착하면 비만세포에서 히스타민 과립체가 방출되어 비강 점막층이 붓고, 비강의 모세혈관이 충혈 되고, 콧물이 나고, 코가 가렵고, 눈이 붉어지고 가렵고, 코가 막히고, 입을 벌리고 숨을 쉬는 증상 징후가 생기는 것이 보통이다.
알레르기 비염이 장기간 지속되면 알레르기 설루트, 알레르기 샤이나, 부정교합 등의 증상 징후가 생길 수 있다.
심하면 아데노이드 안모도 생길 수 있다.
Q.
미국에서 알레르기 비염을 치료하는 데 드는 연간 의료비가 어느 정도인가?
A
연간 4억 5천만불의 진료비가 소요된다고 합니다.
Q.
만성 알레르기 비염이 있는 아이들에게 나타날 수 있는 증상 징후에는 어떤 것이 있는가요.
A.
이상 설명한 여러 가지 주 증상 징후 이외 때로는 수면장애, 학습 장애, 집중력 결여증(주의력 결핍 장애) 및, 또는 행동과다증(과다활동장애), 아데노이드 비대, 편도비대, 목 앞 림프절 비대, 아데노이드 안모, 폐쇄성 수면 무호흡증(수면차단 무호흡증), 이갈기, 부정교합, 다 체모증, 손바닥 과다 잔금, 알레르기 설루트 (Allergic Salute), 콧등 횡선(Dennie’s Lines), 코 폴잎 등의 증상징후가 생길 수 있습니다.
Q.
알레르기 비염을 앓는 아이들에게 더 잘 생길 수 있는 다른 병도 있나요.
A.
부비동염과 기관지 천식, 눈 알레르기, 중이염, 결막염 등이 동시 생기기도 합니다.
Q.
아토피 체질이란 무엇입니까?
A.
전형적인 정상 체질이 아닌 체질을 아토피 체질 또는 아토피라고 합니다.
요즘 아토피 체질이 아닌 사람은 거의 없는 것 같습니다.
아토피 체질을 가진 아이들은 알레르기 비염, 기관지 천식(천식), 아토피 피부염, 옻 접촉성 피부염, 두드러기 등 알레르기 질환에 더 잘 걸리고 아토피 체질인 아이들에게는 식품 알레르기도 더 잘 생깁니다.
Q.
알레르기 비염과 기관지 천식은 어떤 관련이 있는가요.
A.
기관지 천식(천식)이 있었던 과거 병력이 있는 아이들의 90%에게 알레르기 비염이 유발될 수 있고 알레르기 비염이 잘 치료되면 기관지 천식도 잘 치료될 수 있다고 합니다.
알레르기 비염을 앓는 환아들에게 기관지 천식이 생기는 빈도는 알레르기 비염이 없는 아이들에게 기관지 천식이 생기는 빈도보다 3배 이상 더 높다.
알레르기 비염을 앓는 환아들은 기관지 천식을 앓을 확률이 40%라고 한다.
알레르기 비염과 기관지 천식은 IgE, 사이토카인, 히스타민, 류코트리엔 등 생화학 매개로 인해서 유발되고 기관지 천식은 코르티코스테로이드제, 기관지확장제, 항류코트엔제, 항 IgE제 등으로 치료될 수 있고 알레르기 비염은 기관지 천식을 치료하는데 쓰는 약물의 성분이 든 알레르기 비염 약물로 잘 치료될 수 있습니다.
Q.
계절적 알레르기 비염, 통년성 알레르기 비염, 혼합형 알레르기 비염이란 무엇인가?
A.
곰팡이나 몰드 등의 항원으로 유발된 알레르기 비염이 있는 아이들이 곰팡이나 몰드가 자라지 않는 건조한 장소에 가면 곰팡이나 몰드로 알레르기 비염이 더 이상 유발되지 않는 것이 보통입니다.
그 아이들이 곰팡이나 몰드가 자라는 습한 장소에 또 다시 가면 곰팡이나 몰드 항원으로 알레르기 비염이 또 다시 유발되는 것이 보통입니다.
곰팡이나 몰드로 유발되는 알레르기 비염의 증상 징후는 여름철과 같이 곰팡이나 몰드가 자라기 좋은 기온이나 계절에서 더 심해질 수 있습니다.
또 아카시아 화분으로 알레르기 비염이 유발되어 알레르기 비염으로 고생하는 아이들은 아카시아 꽃이 만발하는 5~6월에 아카시아 꽃 화분으로 알레르기 비염이 해마다 유발될 수 있습니다.
이와 같이 계절에 따라 유발되는 알레르기 비염을 계절적 알레르기 비염이라고 합니다.
레그위드(Ragweed)가 자라는 가을철에는 레그위드 꽃가루 항원에 의해서 유발되는 알레르기 비염이 유발될 수 있고 미 뉴잉글랜드 지방에서는 봄에 많이 피는 메이풀 트리 꽃가루 항원으로 봄철에 알레르기 비염이 많이 유발됩니다.
이런 종류의 알레르기 비염을 통틀어 계절적 알레르기 비염이라고 합니다.
거의 매일 접촉되는 집 먼지, 집 먼지 좀 진드기나, 몰드, 또는 곰팡이, 또는 거의 매일 먹는 음식물 등의 항원으로 알레르기 비염이 가장 많이 유발될 수 있습니다.
그런 종류의 항원에 일 년 내내 접촉되는 아이들에게 알레르기 비염 이 일 년 내내 유발될 수 있습니다.
이런 종류의 알레르기 비염 을 통년성 알레르기 비염 이라 합니다. 집 먼지 좀 진드기로 인해 유발되는 통년성 비염(일 년 내내 증상이 있는 알레르기 비염 )은 9세 이전 아이들에게는 잘 발생되지 않습니다.
많은 아이들에게 계절적 알레르기 비염 도 생기고 통년성 알레르기 비염이 함께 있습니다.
이러한 알레르기 비염을 혼합형 알레르기 비염이라고 합니다.
Q.
감기나 스트레스와 알레르기 비염의 증상 징후에 서로 어떤 관계가 있나요.
A.
일반적으로, 감기나 독감 등 바이러스성 상기도 감염병에 걸리거나 스트레스를 많이 받을 때는 알레르기 비염의 증상징후가 훨씬 더 심해질 수 있습니다.
또 더 많은 종류의 항원에 더 많이 노출될 때 그 증상 징후가 더 심해질 수 있습니다.
Q.
급성 알레르기 비염의 전형적 증상징후는 무엇 인가요
A.
나이, 항원의 종류, 합병증의 유무 등에 따라 다릅니다.
알레르기 비염의 전형적인 증상은 다음과 같습니다.
콧물이 나고
코가 막히고 가렵고
재채기 하고
눈이 붉고 가렵고 눈물이 날 수 있고
입천장이 가려울 수 있고
이런 증상이 계절에 따라 재발될 수 있고
이런 증상이 일시적으로 유발될 수 있고 한 계절 내내 유발될 수도 있습니다.
그런 증상이 경도로, 중등도로, 또는 중증도로 나타날 수 있습니다.
Q.
신생아나 영아에게도 알레르기 비염은 생길 수 있나요.
A.
이론적으로, 알레르기 비염의 증상징후는 신생아기부터 시작될 수도 있고 그 후 어느 연령층에서도 시작될 수 있습니다.
우유 단백질이 든 인공영양을 먹기 시작하면, 특히 아토피 체질을 가진 신생아에게 알레르기 비염이 유발되기 시작합니다.
모유를 먹는 아기에게 알레르기 비염이 덜 생길 수 있지만 수유모가 먹은 음식물에 따라 알레르기 비염이 신생아에게도 생길 수 있고 영유아에게도 유발될 수 있습니다.
Q.
우유나 우유 음식물로 유발될 수 있는 알레르기 비염의 발생률은 얼마나 되나요
A.
우유나 우유로 만든 음식물로 유발되는 알레르기 비염의 발병률은 0.3% 정도입니다.
Q.
아토피 체질이 있는 신생아들과 영아들이 먹는 인공영양과 알레르기 비염과 어떤 관련이 있나요
A.
신생아나 영아, 특히 아토피 체질이 있는 신생아와 영아가 우유 단백질이 든 인공영양, 전우유(전유/Whole milk), 우유 음식물을 먹으면 우유 단백질로 알레르기 비염이 유발될 수 있습니다.
Q.
여러 가지 항원들에 한꺼번에 노출되면 알레르기 비염이 더 심해질 수 있는가요.
A.
우유 음식물에 알레르기 비염이 있는 아이들이 집 먼지 좀 진드기에 노출될 때 집집 먼지 좀 진드기 항원으로 알레르기 비염이 유발될 가능성이 더 있고, 또 우유 단백질로 인한 알레르기 비염 과 집 먼지 좀 진드기로 인한 알레르기 비염이 동시 유발될 수 있습니다.
Q.
“알레르기 설루트“란 말 ?
A.
알레르기 비염으로 코가 가려우면 코를 문지르기 위해 손을 들어 마치 경례하는 자세로 코를 손으로 문지르는 증상징후가 있습니다.
이런 증후를 “알레르기 설루트(Allergy salute)라고 합니다.
Q.
알레르기 비염과 “구강호흡과는 무슨 관계가 있나요.
A.
알레르기 비염로 코가 막히면 입을 벌리고 입으로 숨을 쉴 때가 많습니다.
이런 호흡을 “구강호흡“이라 하고 “게이핑(Gaping)”이라도 합니다.
만성 알레르기 비염이 있으면 밤낮을 가리지 않고 아무 사람들 앞에서나 입을 벌리고 숨을 쉬는 경향이 많습니다.
때로는 그렇게 고생하는 아이들을 보고 “바보”라고 말하는 바보 같은 어른들도 있습니다.
신생아들이나 영아들에게 알레르기 비염이 생기면 코가 자주 막히고 입을 벌리고 숨 쉴 때가 많습니다.
이런 증상을 영어로 게이핑(Gaping)이라 하고 한글로 구강호흡이라 합니다.
알레르기 비염이 적절히 잘 치료되지 않으면 이런 증상 징후가 신생아기 때부터 사춘기까지 계속될 수 있고 성인이 된 후에도 계속 나타날 수 있습니다.
Q.
부정교합과 알레르기 비염과의 관계는?
A
알레르기 비염이 장기간 계속되면서 구강호흡을 하고, 아데노이드가 커지고, 편도도 커지고, 입안, 얼굴의 구조 상호관계의 변화가 생기고 치열도 문제가 생길 수 있습니다.
그리고 심한 부정교합이 생길 수 있습니다.
여기에도 찬반론이 있습니다.
저의 경험으로 보면 부정교합과 알레르기 비염과는 밀접한 관계가 있습니다.
그래서 알레르기 비염 치료는 부정교합 치료에 중요한 역할을 한다고 생각합니다.
Q.
알레르기 비염과 아데노이드 안모는 어떤 관계가 있나요?
A.
알레르기 비염으로 입을 벌리고 숨 쉬는 증상이 장기간 생길 수 있습니다.
뻐드렁니, 옥니, 부정교합 등 치열에 이상이 생길 수 있습니다. 눈, 코, 입, 얼굴, 잇몸 등의 해부학적 얼굴 구조의 상호관계도 변화 가 생기고 이상이 생길 수 있습니다.
그래서 특이한 안모의 상이 알레르기 비염이 있는 아이에게 나타날 수 있습니다.
이런 안모를 아데노이드 안모라고 합니다.
Q.
감기와 알레르기 비염은 어떤 차이가 있나요.
A.
감기는 코, 비강, 인두, 부비동, 아데노이드, 편도 등 상기도 기도 부분에 생기는 바이러스성 감염병입니다.
감기에 걸리면 미열 내지 고열이 나고 인두가 아프고 몸이 아픈 것이 보통입니다.
그 감기는 대개 10일 이내 자연히 낫습니다.
알레르기 비염에 걸리면 비강 내 점막층이 붓고 충혈 되고 코가 막히고 콧물이 나고 재채기를 할 수 있고 코가 막히면 코로 숨을 잘 쉴 수 없기 때문에 입을 벌리고 입으로 숨을 쉴 수 있습니다.
잠도 잘 자지 못합니다.
알레르기 비염은 알레르기성 질환이고 알레르기 비염을 앓을 때는 열이 나지 않고 인두통도 없고 몸이 아프지도 않고 2주 이상 계속되는 것이 보통입니다.
이렇게 감기와 알레르기 비염은 다릅니다.
때로는 이 두 병이 함께 있을 수 있습니다.
Q.
알레르기 비염과 아데노이드 또는 편도와의 관계에 어떤 것이 있나요
A.
아데노이드는 비강의 맨 뒤 부위, 인두의 맨 위 부위에 위치한 일종의 림프조직입니다.
아데노이드는 코를 통해서 들어오는 황원, 세균, 바이러스 등을 잡아 상기도 이외의 체내로 더 이상 들어가지 못하게 하는 감염병 방어기능을 합니다.
콧속을 통해 몸속으로 들어오는 해로운 항원을 잡아 체내로 더 이상 들어오지 못하게 하는 일도 합니다.
이런 기능을 과도하게 하면 결과적으로 아데노이드가 해부학적으로 비대해 집니다.
거의 같은 이치로 입안 양쪽에 있는 편도도 커지게 됩니다.
특히 알레르기 비염이 있는 아이들의 아데노이드와 편도는 비정상적으로 더 많이 커져 있는 것이 보통입니다.
Q.
알레르기 비염이 있는 아이들이 코먹은 소리도 하고 코를 더 자주 곤다는데, 이유는 무엇입니까
A.
알레르기 비염이 있는 아이들의 아데노이드와 편도가 비정상적으로 더 커지고 코가 막혀 구강호흡을 하고 비강, 구개, 치열 등 해부학적 구조에 변화가 생깁니다.
그로 인해서 말을 할 때 코 먹은 소리를 내고 잠잘 때 코를 고는 경우가 많습니다.
특히 학령기 아이들에게 알레르기 비염이 있으면 코가 자주 막힐 수 있고 비강의 후부에 있는 아데노이드와 입안 양쪽에 있는 편도가 비정상적으로 많이 커질 수 있습니다.
그런 이유로도 코를 더 잘 곱니다.
Q.
알레르기 비염이 있으면 코피가 잘 난다고 하는데. 왜 그런가요?
A.
알레르기 비염이 있으면 비강 점막층이 붓고 창백하고 습하고 그 점막층에 있는 모세혈관이 확장됩니다.
재채기를 하든지 기침, 사소한 코 외상, 또는 코를 살짝 문지르기만 해도 코를 자칫 건드리기만 해도 확장된 점막층 모세혈관이 터져 코피가 더 잘 날 수 있습니다.
Q.
알레르기 비염이 있어도 기침을 하나요?
A.
알레르기 비염이 있으면 기침을 간간이 조금 할 수 있습니다. 특히, 밤에 누워 잘 때 콧물이 비강의 후부, 비인두 부위로 흘러가서 그로 인해 인두가 자극돼서 자다가 기침을 간간이 할 수 있습니다.
또 알레르기 비염이 있는 아이들의 30%는 기관지 천식을 동시 앓고 있습니다.
그 때문에도 기침을 할 수 있고 때로는 알레르기 비염과 기관지 천식 이 두 병으로 기침을 할 수 있습니다.
기관지 천식이 있는 아이들의 대부분은 밤에 자는 동안 야간성 기관지 천식이 유발돼서 자다가 기침을 하는 것이 보통입니다.
이런 기침을 여러 날 동안 하는 경우도 있습니다.
이렇게 잘 때 유발되는 기관지 천식 발작을 야간성 기관지 천식이라고 합니다.
알레르기 비염이 있는 아이들이 밤에 자다가 기침을 할 때, 야간성 기관지 천식으로 기침을 하는지, 알레르기 비염으로 기침을 하는지, 또는 알레르기 비염과 야간성 기관지 천식, 이 두 병으로 인해서 기침을 하는지 감별 진단하기가 어려울 때도 있습니다.
Q.
알레르기 비염이 있으면 축농증(부비동염)에 잘 걸릴 수 있나요.
A.
그렇습니다.
알레르기 비염이 있으면 축농증에 더 잘 걸릴 수 있습니다.
비강 점막층과 부비동 점막층은 같은 종류의 점막층 세포로 형성되어있고 부비동과 비강은 작은 자연 통기관을 통해 서로 연결되어 있습니다.
또 알레르기 비염을 일으킨 그 통기관의 점막층이 붓고 그 통로가 알레르기 비염으로 자주 막힐 수 있습니다.
자연 통기관이 막히면 부비동에 세균감염이 쉽게 생겨서 축농증에 더 잘 걸립니다.
비강 주위에 전두동, 사골동, 접형동, 상악동 등 여러 개의 부비동이 얼굴 양쪽에 정상적으로 있습니다.
비강 속과 그 주위에 있는 부비동은 작은 통기관으로 정상적으로 서로 연결되어 있습니다.
그 통기관에 있는 점막층이 알레르기 비염으로 부어 통기관이 막힐 수 있고 그로 인해 부비동염(축농증)이 생길 수 있습니다.
이런 이유로 알레르기 비염이 있는 아이들의 대부분은 부비동염에 더 잘 걸립니다.
Q.
알레르기 비염이 있으면 두통이 자주 생길 수 있나요.
A.
알레르기 비염이 있을 때 부비동과 비강 사이를 연결하는 작은 통기관이 쉽게 막히고 그로 인해 막힌 부비동성 두통(Sinus headache)이 자주 생길 수 있습니다.
또 축농증이 생겨 축농증의 증상 징후로 두통이 생길 수 있고 아토피 체질이 있는 아이들에게 긴장성 피로 증후군이 생길 수 있고 그로 인해서도 두통이 자주 생길 수 있습니다.
Q.
알레르기 비염이 있으면 중이염에 더 잘 걸릴 수 있나요
A.
더 잘 걸릴 수 있습니다.
알레르기 비염으로 후비공 부위에 있는 구씨관 입구(이관 입구)와 이관이 부어 이관이 자주 막힐 수 있습니다.
이때 중이 강 속에 음압이 생길 수 있습니다.
중이 강 속에 삼출액이 고일 수 있고 중이염이 생길 수 있습니다.
또 그에 따라 중이 강 삼출액에 세균 감염이 생겨 급성 중이염이 생길 수 있습니다.
구씨관(이관)이 부어 이관이 자주 막힐 수 있고 이관을 통해 중이강과 비인두에 있는 이관 입구 사이에 공기가 유통되지 않을 수 있습니다.
급성 중이염, 또는 삼출성 중이염에 자주 걸릴 수 있습니다.
때로는 청력 이상이 생길 수 있습니다.
Q.
알레르기 비염이 있을 때 나는 콧물과 축농증이 있을 때 나는 콧물에 차이가 있는가요.
A.
합병증이 없이 알레르기 비염만 있을 때는 맑은 콧물이 주로 나오는 것이 보통입니다.
그러나 알레르기 비염과 박테리아 부비동염이 동시 있을 때는 콧물이 누렇거나 퍼렇고 더 짙은 콧물이 나는 것이 보통입니다. 어떤 때는 콧물에 차이가 없습니다.
Q.
알레르기 비염이 있으면 콧물이 꼭 나오나요.
A.
알레르기 비염만 있을 때도 콧물이 안 나올 수 있고 부비동염만 있을 때도 콧물이 안 나올 수 있습니다.
또는 두 가지 병이 동시에 있을 때도 맑은 콧물이 조금씩 나올 수 있고, 때로는 콧물이 조금도 나지 않을 수 있습니다.
Q.
알레르기 비염이 있으면 눈과 입에도 알레르기 질환이 생기나요?
A.
생길 가능성이 많습니다.
눈, 부비동, 아데노이드, 편도, 인두, 구강 등에 알레르기성 질환이 동시에 유발될 수 있습니다.
예를 들면, 알레르기 결막염이 잘 생길 수 있습니다.
알레르기 결막염으로 결막이 자주 충혈 되고 눈이 빨갛고 눈물이 자주 나고 눈이 가려워 눈을 자주 비빌 수 있는 증상 징후들이 생길 수 있습니다.
알레르기 비염으로 지도형 혀가 자주 생길 수 있습니다.
Q.
알레르기 비염이 있는 아이들의 일부는 수면 중 숨이 막혀 무호흡증이 생길 수 있고 때로는 괴롭게 숨을 쉬거나 코를 골 수 있다는 말을 들었는데, 왜 그런가요.
A.
아토피 체질이 있는 아이들의 아데노이드는 아토피 체질이 아닌 아이들의 아데노이드보다 훨씬 더 크고 비대 되어 있는 것이 보통입니다.
또 편도도 마찬가지로 더 커져 있는 경우가 보통입니다.
그 때문에 알레르기 비염이 있는 아이들의 상기도, 즉 숨통이 훨씬 더 좁아집니다.
그래서 수면 중 숨이 잠시 막혀 괴롭게 숨 쉬거나 코를 골 수 있습니다.
때로는 차단성 무호흡증(폐쇄성 수면 무호흡증)도 생길 수 있습니다.
Q.
알레르기 비염이 있는 아이들의 일부에서 아래턱 바로 밑 목에 있는 림프절이 커져 있다는 글을 읽었는데, 왜 그런가요.
A.
알레르기 비염이 있는 아이들의 아래턱 바로 밑에 있는 목 부위에 있는 림프절이 커져있는 것이 보통입니다.
아래턱 바로 밑 목 부분 림프절도 아데노이드와 편도도 일종의 림프조직이고 그 림프조직은 항원들이나 세균이 입이나 비강을 통해 비, 인두 강을 거쳐 몸속으로 더 이상 들어가지 못하게 하는 감염병 방어기능을 합니다.
그런 방어기능을 하다보니까 편도, 목에 있는 림프절도 과다히 커집니다.
Q.
알레르기 비염이 있는 아이들의 대부분이 밤에 자다가 이를 자주 가는 버릇이 생긴다는 데요. 왜 그런가요.
A.
알레르기 비염이 있으면, 눈과 코뿐만 아니라 인두와 입천장도 가려울 수 있습니다.
자다가 인두나 입천장 등이 가려울 때 위턱과 아래턱을 놀리어 가려움증을 해결하는 방법으로 무의식적으로 이를 간다고 주장하는 의사들도 있고 저도 그렇다고 생각합니다.
알레르기 비염이 있는 아이들의 대부분이 밤에 자다가 이를 자주 가는 버릇이 있습니다.
Q.
알레르기 비염이 있으면 구강, 얼굴 등에 어떤 변화가 생길 수 있나요.
A.
코가 자주 막혀 입을 벌리고 숨을 쉬기 때문에 구강, 얼굴, 코, 턱, 치아, 잇몸 등에 해부학적 구조의 상호 관계에 많은 변화가 알레르기 비염이 있는 아이들에게 생길 수 있습니다.
그 결과로 생긴 치아 변화 중 하나가 부정교합입니다.
둘째는 아데노이드 안모입니다. 전에 이미 언급했습니다.
그 외 여러 가지의 변화가 얼굴에 생길 수 있습니다.
Q.
알레르기 비염이 있는 아이들에게 때로는 체모가 더 많이 난다고 하는 데, 왜 그런가요.
A.
항원이 경구, 비강, 피부나 점막층을 통해 체내로 들어옵니다. 그런 피부를 통해 들어오는 항원이 더 이상 체내로 들어오지 못하게 방지하기 위해 체모가 더 많이 나는 것입니다.
콧구멍 속 털도 더 많이 나는 것도 거의 같은 이치입니다.
Q.
알레르기 비염을 어떻게 진단하나요?
A.
현재의 병력, 과거병력, 가족병력, 증상 징후, 진찰 소견 등을 총 종합해 진단하는 것이 일반적입니다.
필요에 따라, 알레르기 유발 검사, 알레르기 피부 시험, 혈액검사 등 다른 여러 가지 방법으로 진단합니다.
Q.
알레르기 비염이 있는 아이들이 감기에 걸리면 알레르기 비염이 없는 아이들과 달리 앓나요?
A.
알레르기 비염이 있는 아이들이 감기에 걸리거나 다른 종류의 바이러스성 상기도 염에 걸리면 알레르기 비염의 증상 징후가 더 악화될 수 있습니다.
그리고 감기 등 상기도염의 증상 징후가 훨씬 더 심하게 나타날 수 있습니다.
Q.
알레르기 비염이 있으면서 흔히 생기는 합병증과 공존이환에는 어떤 것이 있나요.
A.
알레르기 비염이 있으면 아이들은 기관지 천식, 부비동 염, 중이염, 아토피성 피부염, 음식물 알레르기, 약물 알레르기, 곤충 알레르기 등의 공존이환이 있을 수 있습니다.
Q.
알레르기 비염을 진단하는 데 아주 중요한 징후 증상에는 어떤 것이 있나요.
A.
코가 가려워서 코를 추켜올리면서 코를 문지르는 버릇으로 코의 경골과 연골이 연결되는 콧등 피부 부위에 가로로 피부 주름살이 잡힐 수 있습니다. 피부 주름살을 데니 선(Dennie lines)이라고 합니다.
손을 추켜올려 코를 문지르는 징후를 ‘알레르기성 경례‘ 또는 ‘알레르기성 설루트(Allergy salutes)라고 합니다.
두 눈 아래 눈꺼풀의 바로 밑에 있는 피부색이 거무스름한 피부색으로 변합니다.
알레르기성 샤이너(Allergic shiners)라고 한다.
알레르기성 샤이너는 일시적으로 생길 수도 있고 한 번 생긴 후 몇 개월 동안 또는 그 이상 오랫동안 계속 갈 수도 있습니다.
샤이너란 말은 얼굴이나 신체 어떤 부위가 타박상을 입었을 때 타박상을 입은 후 피부색이 거무스름하게 일시적으로 변화된 것을 의미합니다.
알레르기 비염이 오랫동안 지속 될 때 코, 비강 속, 입 속, 아데노이드, 편도 등의 해부학적 상호 관계가 특이하게 변화됩니다.
얼굴 모양이 마치 바보 얼굴 모양으로 변할 수 있다.
이런 얼굴 모양을 아데노이드 얼굴형, 또는 아데노이드 안모(Adenoid face)라고 합니다.
이상 징후는 알레르기 비염을 진단하는데 상당한 가치가 있습니다.
Q.
알레르기 비염을 어떻게 진단하나요?
A.
이미 설명 했지만 환아의 과거와 현재의 병력, 가족 병력, 증상, 징후, 진찰소견 등을 종합해서 주로 진단합니다.
필요에 따라 혈액 검사, 알레르기 피부 시험, 비경 검사. 비강 내시경 등으로 비강을 검진해서 진단합니다.
전형적 알레르기 비염의 증상과 징후가 있고 결막이 충혈 되고 비경으로 비강을 검진할 때 비강 점막이 창백하고 비정상적으로 습한 징후 등이 있으면 이 병을 진단하는데 많은 도움이 됩니다. 그 외 이관이 자주 막히고 기침을 간간이 하고 부비동이 있는 부위에 압박감 등의 증상이 있을 수 있습니다.
Q.
알레르기 비염을 진단하는데 가족 병력이 중요한가요
A.
친 부모 형제자매들 중 누군가에게 기관지 천식, 알레르기성 피부염, 알레르기 비염, 약물 알레르기, 접촉성 피부염, 음식물 알레르기 등 알레르기성 질환이 있는 가족 병력이 있으면 알레르기 비염을 진단하는데 많은 도움이 됩니다.
그리고 친 부모형제자매 중 누구든지 아토피 체질이 있으면 진단하는 데 많이 도움 됩니다.
Q.
알레르기 비염이 음식물 항원으로 인해서도 유발될 수 있는지 어떻게 알지요?
A.
알레르기 비염은 체 염색체 우성으로 유전된다.
알레르기 비염이 음식물 항원으로 인해서도 유발될 수 있습니다.
알레르기 비염을 유발 시키는 음식물에는 어떤 것이 있나 알아내는 방법 중 하나가 유발 검사입니다.
또 그 음식물을 먹는 것을 피해서 진단할 수 있습니다.
Q.
유발 검사란 무엇입니까
A.
음식물 항원으로 유발된 알레르기 비염을 진단하는데 유발 검사로 진단하기도 합니다.
알레르기 비염을 유발시킨다고 의심되는 음식물을 2∼4주 동안 일체 먹지 말고 그 음식물을 2∼4주 먹지 않는 동안 알레르기 비염의 증상 징후가 좋아지는지, 다 없어지는지, 더 하는지, 변화가 없는지 조심스럽게 관찰합니다.
이때 알레르기 비염의 증상징후가 확연히 호전되면 그 음식물이 알레르기 비염을 일으켰을 가능성이 많다고 생각할 수 있습니다.
그러나 이런 방법으로 진단은 확실히 내릴 수는 없습니다.
그 다음 알레르기 비염을 유발시켰다고 의심했던 음식물을 다시 먹을 때 알레르기 비염의 증상징후가 전과 거의 같이 다시 생기면 그 음식물은 알레르기 비염을 유발시켰을 가능성이 아주 많다고 생각할 수 있습니다.
이런 식으로 알레르기 비염을 유발시킨 음식물(항원)을 찾아내서 알레르기성 질환을 진단하는 방법을 유발 검사(도전 검사)라고 합니다.
유발 검사는 아무 때니 해서도 안 되고 부모나 환자의 마음대로 해서는 절대로 안 됩니다.
알레르기 비염이 경미할 때도 의사의 지시에 따라서 의사가 유발 검사를 할 수 있습니다.
Q.
집 먼지나 집 먼지 좀 진드기 등 항원으로 알레르기 비염이 유발된다고 의심할 때 유발 검사(도전 검사)를 할 수 있나요.
A.
할 수 있지요.
집 먼지나 집 먼지 좀 진드기 등의 항원으로 유발되서 알레르기 비염이 있던 아이들이 집 먼지나 집 먼지 좀 진드기가 많은 집안에 있을 때는 코가 가렵고 재채기를 많이 하면서 알레르기 비염의 증상징후이 나타날 수 있습니다.
이와 같이 알레르기 비염의 증상 징후가 나타날 때 집 먼지나 집 먼지 좀 진드기 항원에 알레르기 비염이 유발됐다고 의심할 수 있습니다.
유발검사로 항원을 찾는 것보다 보통 피부 알레르기 시험으로 항원을 찾는 경우가 더 많습니다.
Q.
알레르기 비염을 진단하는 데 쓰는 임상검사는 어떤 것이 있나요.
A.
IgE 혈액검사,
비강 점액검사,
알레르기 피부 검사,
혈액 호산구 검사,
방사선 알러젠 흡수면역 측정법(RAST),
섬유광시 비경 검사,
비강내 도발 검사,
비강 내 공기 유통검사,
비강 내시경 검서
비강 점막층 혈류 검사 등으로 알레르기 비염을 진단할 수 있습니다.
일반적으로, 소아청소년과에서는 이런 검사로 진단하지 않고 알레르기 비염의 증상 징후의 유무, 진찰소견 등을 종합해서 알레르기 비염을 진단하는 것이 보통입니다.
Q.
환경 콘트롤 치료와 항원 피하는 치료에 관해서 설명을 해주세요.
A.
알레르기를 유발시킬 수 있는 모든 항원이나 유발인자들을 가능한 한 피하거나 제거하는 방법이
이상적인 치료 방법입니다.
구체적으로 더 설명하면 다음과 같습니다.
알레르기 비염이나 다른 여러 종류의 알레르기 질환을 유발시킬 수 있는 항원– 음식물을 될 수 있는 한 먹지 말아야 합니다.
알레르기 질환이 있거나 아토피 체질이 있는 친 부모 형제자매들에게 태어난 신생아들이나 영아들에게 우유나 우유 단백질, 또는 콩 단백질이 든 인공영양을 먹이는 대신 가능한 한 모유를 수유하든지 저 알레르기성 인공영양을 먹여 알레르기 비염이 유발되지 않게 예방하고 이미 생긴 알레르기 비염을 적절히 치료합니다.
알레르기 비염과 다른 알레르기 질환을 예방하기 위해 알레르기 질환을 잘 유발시킬 수 있는 그 외 음식물도 될 수 있는 한 먹지 말아야 합니다.
특히, 우유, 달걀, 초콜릿 등 음식물은 알레르기 비염을 비롯한 다른 종류의 알레르기성 질환을 도 잘 유발시킬 수 있는 음식물로 잘 알려져 있습니다.
그런 음식물을 될 수 있는 대로 피합니다. 때로는 알레르기 비염을 일으키는 음식물을 갈망하는 증상도 생길 수 있으므로 주의가 요합니다.
개, 고양이, 새 등의 애완동물을 가능하면 집 안에서 기르지 말고 접촉하지 않는 것이 좋습니다.
부득이, 애완동물을 집안에서 키울 때는 동물의 털, 침, 비듬, 깃털 등에 접촉되거나 흡입되지 않게 하고 개를 자주 목욕시킵니다.
아토피 체질이 있거나 알레르기 비염이 있는 아이들이 사는 집안에 화초나 나무 등을 될 수 있는 한 기르지 말아야 합니다.
곰팡이나 몰드는 지하실 등 습한 곳에서 자라므로 집안의 습도를 적절히 조절해서 곰팡이나 몰드가 자라지 않게 합니다.
고정시켜 깐 카펫에 집 먼지가 더 많이 낄 수 있고 집안 먼지 진드기가 더 잘 자랄 수 있기 때문에 거두어 자주 빨아 쓸 수 있는 카펫을 깔든지 카펫을 깔지 않는 것이 더 좋습니다.
커튼을 자주 빨아 써야 한다.
집안 집 먼지를 깨끗이 청소하고 집 먼지 좀 진드기가 자라지 않도록 합니다.
알레르기 비염이나 아토피 체질이 있는 아이들이 자는 침실에는 침구 이외 다른 것을 놓아서는 안 됩니다.
침대 매트리스와 스프링 박스를 플라스틱 커버로 씌워 집 먼지 좀 진드기가 자라지 않도록 합니다.
꽃이 만발하는 봄철에는 꽃가루나 곰팡이 등이 집안으로 들어오지 않게 창문을 꼭 닫습니다.
화초를 가꾸거나 잔디를 깎을 때 꽃가루나 곰팡이 등이 기도 속으로 흡입될 수 있고 그로 인해 알레르기 비염이나 알레르기성 결막염, 또는 기관지 천식이 유발될 수 있습니다.
그런 항원접촉을 절대적으로 피하기는 어렵지만 가능한 한 접촉을 피합니다.
필요에 따라 마스크를 착용하고 먼지가 눈으로 들어오는 것을 막는 안경을 쓰고 잔디를 깎아야 합니다.
레그위드 꽃이 피는 계절에는 레그위드 잡초가 자라는 곳에 가지 않도록 합니다.
동물의 털, 새 깃털로 만든 옷을 입지도 말고 깃털이나 털을 넣은 베개나 이불 등을 절대로 쓰지 않도록 합니다.
HEPA 공기 필터나 Acaricides 등으로 집 먼지 좀 진드기 등을 감소시킵니다.
바퀴벌레를 박멸시킵니다.
Q.
알레르기 비염 약물 치료에 대해서 알고 싶습니다
A.
항히스타민제-1세대 항히스타민과 2세대 항히스타민이 있습니다.
항염증제 치료,
항원 면역요법
류코트레인 수용체 길항제 (Leukotriene receptor antagonists) 치료.
코르티코스테로이드제 치료.
비만 세포(마스터 세포) 안정제 치료.
비강 속에 직접 넣는 비강 점막 충혈완화제 치료.
알파 아드레날린 작동제 치료.
혼합제 치료.
Q.
알레르기 비염 약물 치료에 쓰는 항히스타민제에 관해 말씀을 해주세요.
A.
항히스타민제는 비만세포(마스터 세포)와 호염기성 세포에서 나오는 히스타민이 세포 섭수체에 결합되지 못하게 차단시켜 알레르기성 질환을 치료하는 데 쓰는 약물을 통틀어 항히스타민제라고 합니다.
항히스타민제는 1세대 항히스타민제와 2세대 항히스타민제로 나누어집니다.
페리액틴(Periactin), 클로트리메톤(Chlor-trimeton), 베나드릴(Benadryl), 피비지(Pyribenzamine) 등의 항히스타민제는 1세대 항히스타민제입니다.
1세대 항히스타민제 중 단 한 종류를 선택해 알레르기 비염을 치료할 수 있습니다.
1세대 항히스타민제로 치료할 때 알레르기 비염의 치료 효과도 있고 진정제, 수면제 효과도 있어 졸린 증상 등 여러 가지 부작용이 생길 수 있습니다.
그래서 요즘에는 2세대 항히스타민제로 알레르기 비염을 주로 치료할 때가 더 많습니다.
클라리틴(Claritin),
애스테미졸(Astemizole),
세티리진(Cetirizine),
페소페나딘(Fexofenadine),
로라타딘(Loratadine) 등은 2세대 항히스타민제입니다.
2세대 항히스타민제로 알레르기 비염을 치료할 때 치료 효과도 좋고 진정 효과는 적고 졸린 증상 등 부작용이 적게 나타날 수 있습니다.
항히스타민제로 알레르기 비염을 치료하면 콧물 나는 증상, 재채기 하는 증상, 코가 가려운 증상, 눈물 나는 증상은 많이 좋아집니다.
비강 점막 충혈완화 효과는 아주 적은 것이 2세대 히스타민 치료제의 단점입니다.
그런 이유로, 저녁에 잠자러 들어가기 전에는 1세대 항히스타민제를 복용하고 낮에는 2세대 항히스타민제로는 치료하는 방법들도 있습니다.
Q.
알레르기 비염 약물 치료에 쓰는 항염증 약물 치료에 관해 말씀을
A.
항히스타민제는 히스타민의 작용을 못하게 해서 알레르기 비염을 치료할 수 있습니다.
그러나 비강에 생긴 염증은 치료되지 않습니다.
그런 염증을 치료하기 위해서 항염증 약물을 사용합니다.
항염증 약물에는 부데소나이드(Budesonide), 플우티카손(Fluticasone), 반세나제(Vancenase Aq Nasal Spray 0.084%), 베클로메타손(Beclomethasone) 등이 있습니다. 그런 약을 비강 점막에 뿌리는 코르티코스테로이드제 코 분무제로 알레르기 비염을 치료할 수 있습니다
Q.
1세대 항히스타민제로 치료할 때 생기는 부작용은
A.
어떤 종류의 항히스타민제로 치료하든 그 항히스타민제로 알레르기 비염을 치료 하는 중 부작용이 생길 수 있고 그 부작용은 항히스타민제의 종류에 따라 다릅니다.
알레르기 비염이나 다른 알레르기 질환을 1세대 항히스타민제로 치료할 때 수면작용, 진정작용, 정신집중이 잘 되지 않은 부작용도 있고, 침이 마르는 등의 부작용도 생길 수 있습니다.
그러나 2세대 항히스타민제로 치료할 때는 그런 부작용이 덜 생기는 것이 보통입니다.
Q.
항히스타민제로 치료할 때 한 종류의 항히스타민제로만 치료하나요?
A.
알레르기 비염을 항히스타민제로 치료할 때 한 종류의 항히스타민제로 잘 치료될 수 있지만
때로는 두 종류의 항히스타민제로 동시 치료해야 치료 효과가 더 잘 나타날 때도 있습니다.
항히스타민제, 비점막층 충혈완화제, 항염증제를 같이 써서 치료할 때도 있습니다.
Q.
한 종류의 항히스타민제로 치료할 때 내성이 생길 수 있나요
A.
있습니다.
알레르기 비염의 증상 징후와 정도에 따라 여러 종류의 1세대 항히스타민제 중 1~2 가지를 선택해서 치료할 수 있습니다.
1세대 항히스타민제로 알레르기 비염을 치료할 때 치료 시작 후 처음 얼마동안은 치료효과가 잘 나타나다가 얼마 후에는 치료효과가 더 이상 나타나지 않으면 의사의 지시에 따라 그 1세대 항히스타민제로 더 이상 계속 치료할 필요가 없을 때도 있습니다.
한 종류의 항히스타민제로 알레르기 비염을 치료할 때 치료효과가 좋으면 필요에 따라 그 약으로 계속 치료할 수 있습니다.
또 한 종류의 항히스타민제로 치료할 때 치료효과가 처음 얼마동안은 아주 좋았다가 같은 항히스타민제로 장기간 계속 치료하면 치료효과가 점점 떨어질 수 있고 나중에는 아주 치료효과가 없어지는 경우도 있습니다.
그래서 다른 종류의 항히스타민제로 바꿔 치료하는 경우도 있습니다.
Q.
알레르기 비염을 항히스타민제로 선택할 때 주의 할 점은 무엇이 있나요
A.
알레르기 비염을 항히스타민제로 치료할 때도 어디까지나 의사의 진단 처방에 따라서 적절한 항히스타민제를 선택해서 치료하는 것이 이상적입니다
Q.
2세대 항히스타민의 대표적인 것은 무엇이 있나요
A.
Loratadine(Claritin), Cetirizine(Zyrtec), Fexofenadine(Allegra),
and Desloratadine(Clarinex) 등이 있습니다.
전에는 의사의 처방이 있어야 이런 2세대 항히스타민제로 치료할 수 있었으나 Loratadine(Claritin), Cetirizine(Zyrtec) 등은 의사의 처방 없이 약국에서 사서 치료할 수 있습니다.
2세대 항히스타민제로 알레르기 비염을 치료하면 치료효과도 좋고 잠을 오게 하는 수면부작용도 잘 생기지 않기 때문에 요즘은 1세대 항히스타민으로 치료를 하지 않는 것이 보통입니다.
Q.
2세대 항히스타민의 부작용은?
A.
진정작용이 덜하고 졸린 증상 등 부작용이 아주 적게 생깁니다.
2세대 항히스타민제와 비강 점막층 모세혈관충혈 완화제인 슈다페드제를 종합해서 만든 알레르기 비염 종합치료 약물도 있습니다.
Q.
슈도에페드린(Pseudoephedrine)제로 알레르기 비염을 치료할 수 있는지요
A.
물론입니다.
슈다페드제는 알파 아드레날린 작동제입니다.
슈다페드로 알레르기 비염을 치료하면 비강 점막층 충혈로 인해 점막층이 부어 코가 막히는 증상이 많이 좋아집니다.
이런 종류의 약물들을 비강 점막층 충혈 완화제라고도 합니다.
비강 점막층 충혈 완화제는 경구용 알약(정)과 액체 형태로 된 물약이 있고 비강 속에 분무로 직접 뿌릴 수 있는 분무제도 있고, 또 방울로 비강 속에 떨어트려 넣을 수 있는 비강 적제도 있습니다.
비강 점막층 충혈완화제의 성분만 들어있는 약물도 있고 항히스타민제와 비강 점막 충혈완화제의 성분을 혼합해서 만든 종합 비강 점막층 충혈완화제도 있습니다.
요즘 흔히 쓰는 경구용 슈도에페드린은 비강 점막층 충혈완화제의 일종이고 그 약물 속에는 항히스타민제가 들어 있지 않습니다.
그 약물로 치료할 때 항히스타민제의 약리작용은 없고 비강 점막층 충혈완화제 작용만 있습니다.
경구용 슈도에퍼드린 등 비강 점막층 충혈완화제는 비강 내 점막층 모세혈관을 일시적으로 강제로 수축시켜서 콧물이 덜 나게 하고 비강 내 점막층 충혈을 일시적으로 가라앉혀 비강 속이 크게 뚫리게 하는 작용이 있습니다.
알레르기 비염을 슈다페드로 치료할 수도 있고 항히스타민제와 슈다페드제가 든 종합제로 치료를 할 수도 있습니다.
Q.
알레르기 비염을 치료할 때 쓸 수 있는 종합 알레르기 비염 약물도 있나요?
A.
물론입니다.
1세대 항히스타민제와 알파 아드레날린 작동제를 혼합한 약물로 치료할 수 있습니다.
페리액틴(Periactin),
클로트리메톤(Chlor-trimeton),
베나드릴(Benadryl),
피비지(Pyribenzamine) 등은 1세대 항히스타민제이고 그중 단 한 가지 1세대 항히스타민제를 선택해 알레르기 비염을 치료할 수도 있고 1세대 항히스타민제와 비강 점막층 충혈완화제가 든
론덱(Rondec), 액티페드(Actifed), 날데칸(Naldecon), 노바페드(Novafed), 트리아미닉(Triaminic), 다이메탭(Dimetapp) 등 알레르기 비염 치료용 종합 약물들 중 한 종류를 선택해 알레르기 비염을 치료할 수 있습니다.
이와 같이 알레르기 비염을 치료하는 데 쓰는 “알레르기 약” 속에는 단 한 종류의 항히스타민제가 들어 있을 수 있고, 또 항히스타민제와 비강 점막층 충혈완화제도 함께 들어 있을 수 있습니다.
Q.
알레르기 비염을 치료할 때 쓰는 알레르기 비염 치료 종합 약물로 감기를 치료할 수 있나요?
A.
물론입니다.
감기를 앓을 때 감기의 증상을 경감시켜는 치료에도 이런 종류의 알레르기 비염 치료제로 감기의 증상을 치료하기도 합니다.
주의할 것은 이런 약으로 알레르기 비염이나 감기를 치료할 때도 의사의 처방에 따라 치료해야 합니다.
특히 2세 이하 여유아들은 이런 종류의 알레르기 비염 치료약인 종합 알레르기 비염 약물로 감기 치료를 해서는 안 됩니다.
Q.
알레르기 비염을 치료할 때 쓰는 비강 속에 직접 넣는 비강 점막층 충혈완화제에 관해서
A.
비강 속에 직접 넣는 비강 점막층 충혈완화제로 치료할 수 있습니다.
에이프린(Afrin/oxymetazoline) 코 부무제나 네오시네프린(Neosynephrine) 코 부무제는 비강 점막층 충혈을 완화시키는 작용이 있습니다.
코 방울약(비 점적제)을 비강 속에 떨어트려 넣거나 분무제를 비강 속에 뿜어 비강 점막층 충혈을 완화시켜 알레르기 비염으로 막힌 비강 속을 속히 뚫어줄 수 있습니다.
네오시네프린제에는 코분무제도 있고 코 점적제도 있습니다.
에이프린제에는 코 분무제도 있습니다.
코 방울약을 비강 점막에 직접 떨어트려 치료하거나 코 분무제로 치료하면 비강 내 점막 충혈이 빨리 일시적으로 경감될 수 있습니다.
약의 종류에 따라 비강 점막층 충혈완화의 효과가 6∼12시간 지속될 수 있고 알레르기 비염으로 막힌 코의 증상이 임시로 좋아질 수 있습니다.
이런 약으로 5일 이상 계속 치료하면 비강 점막이 손상될 수 있습니다. 그러므로
에이프린이 코 분무제나 네오시네프린 코 분무제 등 비강 점막층 충혈 완화제로 치료할 때도 꼭 의사의 처방에 따라서 써야 합니다.
이런 약물은 의사의 처방 없이 약국에서 살 수 있습니다.
Q.
알레르기 비염을 치료할 때 쓰는 비만 세포 안정제는 어떤 약입니까
A.
비만 세포 안정제를 비강 속에 직접 뿌려 비만 세포 속에 잇는 히스타민 과립체가 방출되는 것을 막는 작용이 있습니다.
크로몰린(Cromolyn) 코 분무제는 비만 세포 안정제이고 비만 세포 속 히스타민 과립이 방출되는 것을 막는 약리 작용이 있습니다.
기관지 천식이 유발 되지 않게 예방하는데 크로몰린 코 분무제를 씁니다. 크로몰린 코 분무를 비강 내에 뿌리면 알레르기 비염이 유발되는 것을 예방할 수 있고 이미 생긴 알레르기 비염이 치료될 수 있습니다.
크로몰린 분무제를 비강 내에 뿜어 치료하기가 편하고 예방 효과도 좋습니다.
크로몰린 분무제를 수 주 내지 수개월 동안 계속 써도 예방 효과가 계속 좋습니다.
크로몰린의 분부제의 부작용은 아주 드물게 생깁니다.
처방 없이 사서 쓸 수 있으나 값이 비싼 것이 큰 단점입니다.
Q.
알레르기 비염을 치료할 때 쓰는 코르티코스테로이드제 에 관해
A.
코르티코스테로이드 붐무제 는 소염제 즉 항염증제입니다.
경도의 알레르기 비염은 2세대 항히스타민제를 선택해 우선 치료해 보고 중등도 알레르기 비염이나 중증 알레르기 비염을 치료할 때는 코르티코스테로이드 코 분무제로 우선 선택해 치료해 보는 것이 요즘 경향입니다.
베클로메타손(Beclomethasone), 버드손나이드(Budesonide), 트리암시노론(Triamcinolone) 등의 코르티코스테로이드 코 분무제를 비강 속에 직접 뿌려서 알레르기 비염을 치료하기도 합니다.
베클로메타손 코 분무제나 버드손나이드 코 분무제는 비강 내에 뿌릴 수 있게 만든 분말 형태 분무와 액체형태 분무, 두 가지가 있습니다.
어떤 종류의 코르티코스테로이드 코 분무제는 의사의 처방에 따라 1일 1~2회 양쪽 비강 속에 뿌려 치료합니다.
치료의 경과에 따라 몇 주 내지 몇 달 동안 알레르기 비염을 치료하기도 합니다.
일반적으로 비강 내에 뿌리는 코르티코스테로이드제 코 분무제로 알레르기 비염을 치료할 때 치료효과는 치료 시작한 후 12시간 경부터 나타나기 시작하는 것이 보통입니다.
비 출혈, 안압증가, 녹내장, 신장 성장 지연 등의 부작용이 나타날 수도 있지만 몇 주 동안 계속 치료해도 그런 부작용이 거의 생기지 않는 것이 보통입니다.
특히 코르티코스테로이드 코 분무제로 알레르기 비염을 치료할 때도 의사의 처방에 따라서 그 약을 꼭 써야 합니다.
Q.
코르티코스테로이드제 주사로 알레르기 비염을 치료할 수 있나요
A.
극심한 알레르기 비염이 다른 종류의 치료로 치료되지 않을 때는 경구용 코르티코스테로이드제 나 근육용 Depot corticosteroid제로 며칠 동안 치료할 수 있습니다.
Q.
류코트리엔 수용체 길항제로 치료할 수 있나요?
A.
류코트리엔 수용체 길항제 (Leukotriene-receptor antagonists)로 치료할 수 있습니다.
코 Montelukast sodium (Singulair)으로 치료하면 알레르기 비염의 증상이 확실히 좋아질 수 있습니다.
요즘 류코트리엔 수용체 길항제로 치료하면 자살을 기도하는 경향이 있어 연구 조사하는 중입니다.
Q.
항콜린 작용제( Anticholinergics)로 치료하나요
A.
항콜린 작용제(Anticholinergics)로 치료할 수 있습니다.
Ipratropium bromide (Nasal Atrovent 0.03%) 코 분무제를 비강 속에 뿌려 알레르기 비염을 치료할 수 있습니다.
맑은 콧물이 많이 날 때 이 종류의 약물로 치료하면 치료효과가 좋습니다.
Q.
항히스타민제와 코(비) 코르티코스테로이드제 로 동시 치료할 수 있나요
A.
할 수 있습니다.
항히스타민제와 코르티코스테로이드제로 동시 치료할 수 있습니다.
경구용 항히스타민제로 치료가 잘 되지 않거나 코르티코스테로이드제 코 분무제로 치료가 잘 되지 않는 심한 알레르기 비염을 경구용 항히스타민제와 코르티코스테로이드제 코 분무로 동시 치료하면 치료효과가 아주 좋을 수 있습니다.
Q. 어떤 경우에 항원 면역 요법으로 치료할 수 있나요
A.
적절히 치료를 해도 잘 치료되지 않은 중등도 알레르기 비염이나 중증 알레르기 비염
전신 코르티코스테로이드제의 치료를 요하는 심한 알레르기 비염
적절한 코르티코스테로이드제로 치료를 적절히 해도 치료가 되지 않는 심한 알레르기 비염
부비동염 및, 또는 기관지 천식과 알레르기 비염이 동시 있을 때는 알레르기 비염을 항원 면역 요법으로 치료할 수 있습니다.
Q.
항원 면역 요법에 관해 설명해 주세요
A.
알레르기 비염을 유발시킬 수 있는 고양이 털이나 개의 털이나 비듬, 초목의 꽃가루, 또는 집안 먼지 진드기 등에서 순수한 항원물질을 정제 추출할 수 있습니다.
이렇게 정제 추출된 여러 종류의 항원물질을 알레르기 비염이나 다른 알레르기 질환이 있는 아이들의 피부 표면층에 접촉시키거나 피부층에 주입할 때 나타나는 피부 반응의 정도를 보고 그 아이가 가지고 있는 알레르기 질환이 어떤 종류의 항원으로 인해서 유발됐는지 알아볼 수 있습니다.
알레르기 비염이 있는 아이들에게 시험한 피부반응 검사의 결과에서 알아낸 항원 물질의 극소량을 피하주사로 항원 면역 요법 치료를 할 수 있습니다.
처음에는 최소 극소량의 항원 물질로 면역 요법을 시작해서 점점 그 용량을 항원 면역요법 유지용량까지 증가 시킨다.
항원면역요법 유지용량까지 증가시킨 후부터는 그 유지용량을 2~6주 간격으로 주어 항원 면역치료를 하는 것이 보통입니다.
이런 항원 면역요법으로 치료를 하면 알레르기 비염의 증상이 ⅔ 정도가 경감된다고 합니다. 이와 같이 항원으로 알레르기 비염이 더 이상 생기지 않게 치료하는 법을 항원 면역 요법이라고 한다.
항원 면역 요법은 이론적으로 이상적 알레르기 비염 치료법인 것 같지만 알레르기 비염을 치료할 때 여러 가지 이유로 최초 선택 치료 방법은 아닙니다.
전에 설명한 거와 같이, 알레젠(항원)을 피하거나 제거, 알레르기 치료약물 치료 및, 또는 항원 제거 및 피함 등으로 적절히 치료해도 알레르기 비염의 증상 징후가 잘 치료되지 않거나 증상 징후가 심해져서 잠을 잘 수도 없고 학교나 집에서 공부하는데 지장도 생기고 일상생활에 지장이 많이 생길 때는 알레르기 비염을 항원 면역 요법으로 치료하는 것이 보통입니다.
3세 이전 영유아들의 알레르기 비염은 항원 면역 요법으로 치료되지 않는 것이 일반적입니다.
항원 면역 요법으로 알레르기 비염 치료를 받은 4~14세 연령층에 속하는 아이들에게 기관지 천식이 훨씬 덜 생긴다는 연구 결과도 있습니다.
항원 면역 요법으로 치료할 때 전신 부작용이 5~10% 정도 생길 수 있고 어떤 부작용은 생명을 위협할 수 있습니다.
또 치료비도 상당한 것이 단점입니다.
항원 면역 요법을 피하주사로 하는 것이 보통이지만 서구에서는 혓바닥 밑에 항원을 넣어 항원 면역 요법을 하기도 합니다.
Q.
코르티코스테로이드제 와 2세대 항히스타민제로 치료한 결과는
A.
심한 알레르기 비염은 비강 속에 뿌려 쓰는 코르티코스테로이드 코 분무제와 비 진정효과가 아주 적은 2세대 항히스타민제로 치료하면 치료효과가 아주 좋습니다.
계절성 알레르기 비염의 36~80% 또는 통년성 알레르기 비염의 55~86%는 잘 치료됩니다.
Q.
코브레이션 비갑개 경감치료(Coblation turbinate reduction treatment)란 무슨 치료입니까
A.
만성 알레르기 비염으로 비강 점막층이 충혈되고 비강이 붓고 막힐 수 있습니다.
알레르기 비염이나 다른 원인으로 비갑개가 자극받고 염증이 생기고 비갑개가 커질 수 있습니다. 비강 점막조직 손상을 입히지 않고 붓고 염증이 생긴 비갑개 부피를 감소시키는 외과적 치료방법은 코브레이션 비갑개 경감치료입니다.
코가 막혀 모든 내과적 치료를 해 봐도 효과가 없을 때 이 방법으로 치료를 해볼 수 있다(출처-Pediatric News, July 2007).
Q.
알레르기 비염이 시작되는 나이는 유발 인자에 따라 다르다고 최근 뉴스에서 들었습니다. 그에 대해 설명을?
A.
알레르기 비염이 유발되기 시작되는 나이는 유발 인자에 따라 다릅니다.
알레르기 비염으로 고생하는 것도 문제이거니와 그 치료비도 상당합니다.
그리고 알레르기 비염을 앓는 아이들에게는 부비동염, 코 폴립, 중이염, 수면 문제, 기관지 천식 등이 생기기 쉽습니다.
우유, 달걀, 밀가루 음식, 바퀴벌레, 고양이, 개, 집 먼지 좀 진드기 등이 알레르기 비염을 유발시키는 인자로 “잘” 알려졌습니다.
수면장애, 무호흡증, 집중력 결여증, 공부장애, 생산력 감소 등으로 인해 여러 가지 건강문제가 나타날 수 있습니다.
알레르기 비염은 1세 이전에도 유발될 수 있지만 진짜 알레르기 비염은 1세 이전에는 잘 생기지 않습니다.
알레르기 비염을 일으키는 데 주 역할을 하는 아이쥐이(IgE) 항체는 IgG, IgA, IgM 항체보다 더 늦게 나타나기 때문에 1세 이전에는 알레르기 비염이 잘 생기지 않습니다.
화분으로 인해 유발되는 알레르기 비염은 화분에 노출되기 시작한 후 3년 정도 걸리기 때문에 생후 3세 이전에는 화분 알레르기 비염이 생기지 않는 것이 보통입니다.
집먼지 진드기로 유발되는 통년성 비염(일년 내내 증상이 있는 알레르기 비염 )은 9세 이전에는 잘 발생되지 않습니다.
우유나 우유로 만든 음식물로 인해 유발되는 알레르기 비염은 0.3% 정도입니다.
아토피 체질인 아이들에게서 알레르기 비염의 발생률은 그 이상 될 것입니다.
알레르기 비염이 있는 생후 2세 이하 유아들의 50%에게 기관지 천식도 발생될 수 있습니다. 그러나 그보다 훨씬 높은 빈도로 발생될 것입니다.
Fexofenadine(Allegra), Loratadine(Claritin), Cetirizine(Zyrtec) 등은 비 진정 히스타민제이고 이 약으로 치료하는 동안 진정효과가 잘 나타나지 않습니다.
Azelastine(Astelin)은 항히스타민과 항소염작용이 있고 비강 내에 뿌려 치료하는 약이다. Beclomethasone, Budesonide(RhinocortAqua), Dexamethasone, Flunisolide, Fluticasone Propionate, Mometasone Furoate, Triamcinolone Acetonide 등의 코르티코스테로이드제는 알레르기 비염 치료 코 분무제입니다.
이 코르티코스테로이드제는 항염증작용이 있습니다.
비강 내 뿌려 알레르기 비염을 치료하는데 쓰는 국소적 알레르기 비염치료제들입니다.
Atrovent nasal spray는 비점막층 모세혈관 충혈 완화제이고
Cromolyn sodium 코 분무제는 항염작용(항염증작용)이 있습니다.
나이와 알레르기 비염의 정도에 따라 위에 설명한 약들 중 한 가지나 두 가지 약을 선택해서 알레르기 비염을 치료하면 치료효과가 대단히 좋습니다.
심한 알레르기 비염은 비강 속에 뿌려 쓰는 코르티코스테로이드 코 분무제와 비 진정효과가 아주 적은 2세대 항히스타민제로 치료하면 치료효과가 아주 좋습니다.
계절성 알레르기 비염의 36~80% 또 통년성 알레르기 비염 의 55~86%는 잘 치료됩니다.
Budesonide 코 분무제에 관한 더 자세한 정보는 www.rhinocortaqua.com)에서 더 얻으시기 바랍니다.
One hundred Qs & As on allergy rhinitis
Q. Is allergic rhinitis a hereditary disease?
A. That’s right. It is passed down from generation to generation as somatic dominance. The disease can affect both grandfathers, fathers, sons and daughters in the same household.
Q. Is allergic rhinitis a common disease?
A. 15-22% of Americans of all ages suffer from allergic rhinitis. Another study found that 8.8 to 16 percent of Americans have allergic rhinitis. According to another study, 20-30% of children and adolescents suffer from allergic rhinitis.
Its incidence is on the rise. 10% of American children before puberty, About 20% of adolescents and young adults in the United States have allergic rhinitis.
According to the results of a survey of 13,579 American children and adolescents belonging to the age group 0-17, the incidence of allergic rhinitis was 4.8% in the age group 0-4 years old, 10.5% in the age group 5-11 years old; It was 14.2% in the 12-17-year-old age group. It can be thought that about 10-20 out of 100 children and adolescents suffer from allergic rhinitis. Allergic rhinitis is the most common chronic disease of the respiratory system. pictorial antigen

Figure 3. Allergens that can cause allergic diseases Dog and cat hair, dander, house dust mites (house dust mites), mold, mold, pollen, drugs, fish or shellfish, milk and milk food, eggs, flour food and cosmetics, chocolate, nuts, peanuts, beans, etc. Allergens that can cause allergies are relatively more common. Children with severe allergic rhinitis may develop adenoid facial features (allergic facial features). Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Antigen-II as seen in pictures

photo 4. Foods that may make you more prone to food allergies The most common foods that cause food allergies are eggs, milk, soybeans, fish and shellfish, peanuts, walnuts, and wheat flour. Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Picture 5. The food you see in the picture is easy to cause various allergic diseases. Foods such as milk, milk foods, fish, wheat, and shellfish, and nuts such as eggs, peanuts, and walnuts can cause allergies more often. Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Photo 6. House dust and house dust mites are easy to cause allergic diseases such as allergic rhinitis, bronchial asthma, and atopic dermatitis. Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Q. What are the causes of allergic rhinitis?
A.
As already mentioned, you are born with a genetic factor that is inherited as a somatic chromosomal dominance that can cause allergic rhinitis. In addition, antigens that can cause allergies to enter the body through the nose, oral cavity, mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract, through the skin or mucous membranes, and through other organs in the body, so that antigen-antibody adverse reactions occur in the nasal mucosa. At that time, histamine granules are released from mast cells, and other biochemicals work together to cause allergic rhinitis.
Q. What are the antigens that cause allergic rhinitis?
A. Plant pollen, mold, mold, dog, cat, cow, horse, chicken, bird hair or dander, feathers, saliva, dead insect powder, house dust mites, house Dust can cause allergic rhinitis. Allergens such as milk, eggs, chocolate, wheat flour, soybean, fish, and peanuts ingested orally and through the gastrointestinal tract can enter the blood and reach the mucous membrane of the nasal passages, causing allergic rhinitis. Allergens that enter the body through the skin or the mucous membrane of each organ can cause allergic rhinitis. Allergic rhinitis can develop in the mucous membranes of the nasal passages when cat hair, dander, or saliva is inhaled directly into the nasal passages. When the nasal mucosa is no longer in contact with cat hair, dander, or saliva, it is common for allergic rhinitis to no longer occur due to cat hair, dander, or saliva. When the nasal mucosa layer comes into contact with cat fur, saliva, dander, etc., allergic rhinitis may occur again with cat fur antigens.
Q. What is the mechanism of allergic rhinitis?
A. When an antigen that can cause allergic rhinitis arrives at the nasal mucosa, histamine granules are released from mast cells, and the nasal mucosa is swollen, the nasal capillaries are congested, runny nose, itchy eyes, red and itchy eyes, nose It is common to have symptoms such as blockage of the mouth and breathing with the mouth open. If allergic rhinitis persists for a long time, symptoms such as allergic salt, allergic shine, and malocclusion may occur. In severe cases, adenoids may also develop.
Q. What is the annual medical cost of treating allergic rhinitis in the United States?
A
It is estimated that the annual cost of treatment is $450 million.
Q. What are the possible signs of symptoms in children with chronic allergic rhinitis?
A. In addition to the several main symptoms described above, sometimes sleep disturbance, learning difficulties, attention deficit disorder (attention deficit disorder) and, or hyperactivity disorder (hyperactivity disorder), enlarged adenoids, enlarged tonsils, enlarged anterior neck lymph nodes, adenoid facial, obstructive sleep Symptoms such as apnea (sleep-blocking apnea), bruising, malocclusion, polytheism, excess palmar baldness, Allergic Salute, Dennie’s Lines, and nasal poles may occur.
Q. Are there other conditions that children with allergic rhinitis may be more likely to develop?
A. Sinusitis, bronchial asthma, eye allergy, otitis media, and conjunctivitis may occur simultaneously.
Q. What is atopic constitution?
A. A constitution that is not a typical normal constitution is called atopic constitution or atopic constitution. It seems that there are few people who are not atopic these days. Children with the atopic constitution are more prone to allergic diseases such as allergic rhinitis, bronchial asthma (asthma), atopic dermatitis, poison ivy contact dermatitis, and urticaria, and children with the atopic constitution are more likely to develop food allergies.
Q. What is the relationship between allergic rhinitis and bronchial asthma?
A. Allergic rhinitis can occur in 90% of children with a history of bronchial asthma (asthma), and bronchial asthma can be cured if the allergic rhinitis is well treated. The incidence of bronchial asthma in children with allergic rhinitis is three times higher than that in children without allergic rhinitis. Children with allergic rhinitis have a 40% chance of developing bronchial asthma. Allergic rhinitis and bronchial asthma are caused by biochemical mediators such as IgE, cytokines, histamine, and leukotriene. Bronchial asthma can be treated with corticosteroids, bronchodilators, anti-leukotriene agents, and anti-IgE agents, and allergic rhinitis is bronchial asthma. Allergic rhinitis drugs, which contain ingredients of drugs used to treat rhinitis, can be treated well.
Q. What is seasonal allergic rhinitis, perennial allergic rhinitis, and mixed allergic rhinitis?
A. When children with allergic rhinitis caused by an antigen such as mold or mold go to a dry place where mold or mold does not grow, it is normal that the mold or mold no longer causes allergic rhinitis. If the children go back to the humid place where the mold or mold grows, it is normal for the mold or mold antigen to trigger another allergic rhinitis.
Symptoms of mold or mold-induced allergic rhinitis may be more severe in the temperature or season when mold or mold grows, such as in summer. In addition, children suffering from allergic rhinitis due to allergic rhinitis caused by acacia pollen may develop allergic rhinitis every year with acacia pollen in May to June when acacia flowers are in full bloom. This seasonal allergic rhinitis is called seasonal allergic rhinitis. Allergic rhinitis caused by ragweed pollen antigens can be induced in the autumn when Ragweed grows, and in New England, a lot of allergic rhinitis is induced in the spring with maple tree pollen antigens that bloom in spring. Collectively, this type of allergic rhinitis is called seasonal allergic rhinitis. Allergens such as house dust, house dust mites, molds, or mold that you come into contact with almost every day, or foods you eat almost every day are the most likely triggers for allergic rhinitis. Allergic rhinitis can be induced year-round in children who are exposed to those kinds of antigens year-round. This type of allergic rhinitis is called perennial allergic rhinitis. Perennial rhinitis caused by house dust mites (allergic rhinitis with symptoms all year round) is less common in children younger than 9 years of age. Many children also develop seasonal allergic rhinitis and perennial allergic rhinitis. This type of allergic rhinitis is called mixed allergic rhinitis.
Q. What is the relationship between cold or stress and the symptoms of allergic rhinitis?
A. In general, the symptoms of allergic rhinitis can be much worse when you have a viral upper respiratory infection, such as a cold or flu, or are under a lot of stress. Also, the symptoms can get worse when you are exposed to more types of antigens.
Q. What are the typical symptoms of acute allergic rhinitis?
A. It depends on your age, the type of antigen, and the presence or absence of complications. Typical symptoms of allergic rhinitis include: I have a runny nose stuffy nose and itchy sneeze Your eyes may be red, itchy, and tearful. The roof of the mouth may be itchy These symptoms may recur depending on the season. These symptoms may be temporary or may occur throughout the season. Such symptoms may be mild, moderate, or severe.
Q. Is allergic rhinitis possible in newborns and infants?
A. Theoretically, the symptoms of allergic rhinitis can begin in newborns or at any age thereafter. Allergic rhinitis begins to occur, especially in newborns with atopic constitution, when they start taking artificial nutrition containing milk protein. Although infants who are breastfed are less likely to develop allergic rhinitis, depending on the diet the nursing mother eats, allergic rhinitis can occur in newborns and in infants as well.
Q. What is the incidence of allergic rhinitis that can be caused by milk or milk food?
A. The incidence of allergic rhinitis caused by milk or milk-based foods is about 0.3%.
Q. What is the relationship between artificial nutrition and allergic rhinitis in newborns and infants with the atopic constitution?
A. If newborns or infants, especially those with the atopic constitution, eat artificial nutrition containing milk protein, whole milk, or milk food, milk protein may cause allergic rhinitis.
Q. Can allergic rhinitis worsen when exposed to multiple antigens at once?
A. When children with allergic rhinitis to milk food are exposed to house dust mites, they are more likely to develop allergic rhinitis with house dust mite antigen, and allergic rhinitis caused by milk protein and allergic rhinitis caused by house dust mites can be triggered simultaneously.
Q. What do you mean by “allergic salt”?
A. If your nose is itchy due to allergic rhinitis, there are symptoms of raising your hand to rub your nose and rubbing your nose with your hand in a saluting position. These symptoms are called “allergy salute.”
Q. What is the relationship between allergic rhinitis and mouth breathing?
A. When your nose is stuffy due to allergic rhinitis, you often breathe through your mouth with your mouth open. This breathing is called “mouth breathing” or “gaping”. If you have chronic allergic rhinitis, you tend to breathe with your mouth open in front of anyone, day or night. Sometimes there are stupid adults who see children suffering so much and say “stupid.” Newborns and infants with allergic rhinitis often have a stuffy nose and often breathe with their mouth open. This symptom is called gaping in English and oral breathing in Korean. If allergic rhinitis is not treated adequately, these symptoms can persist from infancy through puberty and continue into adulthood.
Q. What is the relationship between malocclusion and allergic rhinitis?
A
As allergic rhinitis continues for a long time, mouth breathing, enlarged adenoids, enlarged tonsils, changes in the structural interrelationships of the mouth and face, and dentition problems may occur. And severe malocclusion can occur. There are pros and cons here too. In my experience, there is a close relationship between malocclusion and allergic rhinitis. So, I think the treatment of allergic rhinitis plays an important role in the treatment of malocclusion.
Q. What is the relationship between allergic rhinitis and adenoids?
A. Allergic rhinitis can cause prolonged breathing with the mouth open. There may be abnormalities in the dentition, such as cavities, occlusions, and malocclusions. The interrelationship of anatomical facial structures such as eyes, nose, mouth, face, and gums may also change and cause abnormalities. Therefore, unusual facial features may appear in children with allergic rhinitis. This face is called the adenoid face.
Q. What is the difference between a cold and allergic rhinitis?
A. A cold is a viral infection that occurs in the upper respiratory tract, such as the nose, nasal passages, pharynx, sinuses, adenoids, and tonsils. When you catch a cold, it is common to have a low to high fever, sore throat, and body aches. The cold usually goes away on its own within 10 days. If you have allergic rhinitis, the mucosal layer in your nasal passages will be swollen and red, and you may have a stuffy nose, runny nose and sneezing. I can’t even sleep well. Allergic rhinitis is an allergic disease, and when you suffer from allergic rhinitis, there is no fever, no sore throat, no body aches, and it usually lasts more than 2 weeks. There is a difference between cold and allergic rhinitis. Sometimes these two diseases can coexist.
Q. What’s the relationship between allergic rhinitis and adenoids or tonsils?
A. Adenoids are a type of lymphoid tissue located at the back of the nasal passages and at the top of the pharynx. Adenoids act as a defense against infectious diseases by catching sulfur sources, bacteria, and viruses that enter through the nose and preventing them from entering the body any more than the upper respiratory tract. It also traps harmful antigens that enter the body through the nostrils and prevents them from entering the body anymore. Excessive use of these functions results in anatomical enlargement of the adenoids. In almost the same way, the tonsils on either side of the mouth are enlarged. It is common for adenoids and tonsils to be abnormally enlarged, especially in children with allergic rhinitis.
Q. Children with allergic rhinitis also snort and snore more often, why
A. In children with allergic rhinitis, the adenoids and tonsils become abnormally enlarged, the nose becomes blocked, mouth breathing occurs, and changes in the anatomy of the nasal cavity, palate, and dentition occur. As a result, there are many cases of snoring when talking and snoring when sleeping. Allergic rhinitis, especially in school-age children, can lead to frequent nasal congestion and abnormally large adenoids at the back of the nasal passages and tonsils on either side of the mouth. And that’s why I snort better.
Q. It is said that if you have allergic rhinitis, you may have nosebleeds. Why?
A. In allergic rhinitis, the nasal mucosa is swollen, pale, and moist, and the capillaries in that mucous membrane dilate. Even sneezing, coughing, minor nasal trauma, or even a light rub of the nose can cause the enlarged mucosal capillaries to burst, making it easier to bleed.
Q. Do you cough even with allergic rhinitis?
A. If you have allergic rhinitis, you may have a slight intermittent cough. In particular, when sleeping at night, a runny nose flows down the back of the nasal passages and into the nasopharynx, which irritates the pharynx, which may cause intermittent coughing while sleeping. In addition, 30% of children with allergic rhinitis also have bronchial asthma. Because of that too, you can cough, and sometimes you can cough with two diseases: allergic rhinitis and bronchial asthma. Most children with bronchial asthma develop nocturnal bronchial asthma while sleeping at night, so it is common to cough while sleeping. In some cases, this cough can last for several days. This type of sleep-induced bronchial asthma attack is called nocturnal bronchial asthma. Differential diagnosis of children with allergic rhinitis when sleeping at night, coughing with nocturnal bronchial asthma, with allergic rhinitis, or with allergic rhinitis and nocturnal bronchial asthma There are times when it is difficult.
Q. If I have allergic rhinitis, can I easily get sinusitis (sinusitis)?
A. That’s right. If you have allergic rhinitis, you may be more prone to sinusitis. The nasal mucosa and the sinus mucosa are made of the same type of mucosal cells, and the sinuses and nasal passages are connected to each other through small natural vents. In addition, the mucosal layer of the airway that caused allergic rhinitis swells, and the passageway can often be blocked by allergic rhinitis. When the natural ducts are blocked, the sinuses can become more susceptible to bacterial infections, making them more susceptible to sinus infections. Several sinuses, such as the frontal, ethmoid, sphenoid, and maxillary sinuses, are normally present on both sides of the face around the nasal cavity. The sinuses in and around the nasal cavity are normally connected to each other by small vents. The mucosal layer in the duct can swell with allergic rhinitis, which can block the duct, resulting in sinusitis (sinusitis). For this reason, most children with allergic rhinitis are more prone to sinusitis.
Q. Does allergic rhinitis cause frequent headaches?
A. When you have allergic rhinitis, the small air ducts that connect your sinuses and nasal passages are easily blocked, which can often lead to a blocked sinus headache. In addition, sinusitis can cause headaches as a symptom of sinusitis, and tension fatigue syndrome can occur in children with atopic constitution, which can also cause frequent headaches.
Q. Is allergic rhinitis more prone to otitis media?
A. It could take better. Allergic rhinitis can cause frequent blockage of the bulbar duct and the eustachian tube in the posterior nasal cavity. This can create negative pressure in the middle ear cavity. Exudate may accumulate in the middle ear cavity and otitis media may develop. It can also lead to bacterial infection of the middle ear cavity effusion, resulting in acute otitis media. The bulbar canal (ear tube) may swell and block the ear canal frequently, preventing air from passing between the middle ear cavity and the entrance to the ear tube in the nasopharynx. You may often get acute otitis media, or otitis media with effusion. Sometimes hearing loss can occur.
Q. Is there a difference between a runny nose when I have allergic rhinitis and a runny nose when I have sinusitis?
A. When there is only allergic rhinitis without complications, it is normal to have a clear runny nose. However, when allergic rhinitis and bacterial sinusitis coexist, it is common to have a runny nose that is yellow or blue and thicker. Sometimes there is no difference in the runny nose.
Q. Do you have runny nose if you have allergic rhinitis?
A. A runny nose may not come out even when there is only allergic rhinitis, and a runny nose may not come out when there is only sinusitis. Or, even when both diseases are present at the same time, a clear runny nose may come out little by little, and sometimes there may be no runny nose at all.
Q. Does allergic rhinitis cause allergic diseases in the eyes and mouth?
A. It’s very likely to happen. Allergic diseases in the eyes, sinuses, adenoids, tonsils, pharynx, oral cavity, etc. can be triggered at the same time. For example, allergic conjunctivitis may develop. Allergic conjunctivitis can cause symptoms of frequent redness of the conjunctiva, red, watery eyes, itchy eyes, and frequent rubbing of the eyes. Allergic rhinitis can often result in a map tongue.
Q. I’ve been told that some children with allergic rhinitis can choke during sleep, resulting in apnea, and sometimes painful breathing or snoring, and why?
A. It is common for adenoids in children with atopic constitution to be much larger and hypertrophic than those in children without atopic constitution. Also, the tonsils are usually larger as well. Because of this, the upper airways, or breathing, in children with allergic rhinitis become much narrower. This can cause shortness of breath during sleep, making it difficult to breathe or snort. Sometimes obstructive apnea (obstructive sleep apnea) also develops. Q. I read that some of the children with allergic rhinitis had enlarged lymph nodes in the neck just below the lower jaw, why is that?
A. It is common for children with allergic rhinitis to have enlarged lymph nodes in the neck area just below the lower jaw. The lymph nodes in the neck just below the mandible, adenoids, and tonsils are also a kind of lymphatic tissue, and the lymphatic tissue has an infectious disease defense function that prevents antigens or bacteria from entering the body through the nasal and pharyngeal cavities through the mouth or nasal passages. Because of such a defensive function, the lymph nodes in the tonsils and neck also become excessively large.
Q. Most children with allergic rhinitis develop a habit of gnashing their teeth at night. Why?
A. If you have allergic rhinitis, your eyes and nose, as well as your pharynx and roof of your mouth, maybe itchy. There are some doctors who claim that the pharynx or roof of the mouth is itchy while sleeping, and I think that it is the case that people unconsciously grind their teeth as a way to relieve itching by teasing the upper and lower jaws. Most children with allergic rhinitis have a habit of gnashing their teeth at night.
Q. If you have allergic rhinitis, what changes can occur in your mouth and face?
A. Children with allergic rhinitis can experience many changes in the interrelationships of the anatomy of the mouth, face, nose, jaw, teeth, gums, etc., because the nose is often clogged and breathing with the mouth open. One of the resulting tooth changes is malocclusion. The second is adenoid facial hair. I’ve already mentioned it before. Many other changes can occur on the face.
Q. It is said that children with allergic rhinitis sometimes have more body hair, but why?
A. Antigens enter the body through the oral, nasal, or skin or mucous membranes. More body hair is produced to prevent any further antigens from entering the body through that skin. It is almost the same reason that more hair grows in the nostrils.
Q. How is allergic rhinitis diagnosed?
A. It is common to make a diagnosis by integrating the current medical history, past medical history, family history, symptom signs, and examination findings. Depending on the need, the diagnosis is made by several other methods, such as allergen provoking tests, allergic skin tests, and blood tests.
Q. Do children with allergic rhinitis get colds differently from children without allergic rhinitis? A. Symptoms of allergic rhinitis can be made worse when children with allergic rhinitis have a cold or other types of viral upper respiratory tract infections. And the symptoms of upper respiratory tract infections, such as a cold, can be much more severe.
Q. What are the common complications and co-morbidities of allergic rhinitis?
A. Children with allergic rhinitis may have co-morbidities such as bronchial asthma, sinusitis, otitis media, atopic dermatitis, food allergy, drug allergy, and insect allergy.
Q. What are the signs and symptoms that are very important in diagnosing allergic rhinitis?
A. The habit of rubbing the nose while raising the nose because it is itchy can cause horizontal skin wrinkles to form on the skin area of the nose bridge, where the tibia and cartilage of the nose are connected. Skin wrinkles are called Dennie lines. Signs of raising your hand and rubbing your nose are called ‘allergic salutes’ or ‘allergy salutes’. The skin color just under the eyelids under both eyes changes to a dark skin color. They are called allergic shiners. Allergic shiners can be temporary or they can go on for several months or longer. The word “shiner” refers to a temporary change in the color of the skin to darkening after a bruise when the face or any part of the body is bruised. When allergic rhinitis persists for a long time, the anatomical interrelationships of the nose, nasal passages, mouth, adenoids, and tonsils are unusually changed. The shape of the face can change to look like a fool’s face. This face shape is called adenoid face shape, or adenoid face. Anomalies are of considerable value in diagnosing allergic rhinitis.
Q. How is allergic rhinitis diagnosed?
A. As already explained, the diagnosis is mainly made by synthesizing the patient’s past and present medical history, family history, symptoms, signs, and examination findings. Blood tests, allergic skin tests, parenteral tests as needed. Diagnosis is made by examining the nasal cavity with a nasal endoscopy. If there are symptoms and signs of typical allergic rhinitis, the conjunctiva is congested, and the nasal mucosa is pale and abnormally moist when examining the nasal passages, it is very helpful to diagnose this disease. In addition, there may be symptoms such as frequent blockage of the ear canal, intermittent coughing, and a feeling of pressure in the sinus area.
Q. Is a family history important in diagnosing allergic rhinitis?
A. A family history of allergic rhinitis, such as bronchial asthma, allergic dermatitis, allergic rhinitis, drug allergy, contact dermatitis, or food allergy, of any of the biological parents or siblings is very helpful in diagnosing allergic rhinitis. And if any of your biological parents or siblings have atopic constitution, it helps a lot to diagnose.
Q. How do you know if allergic rhinitis can also be caused by food allergens?
A. Allergic rhinitis is inherited as somatic chromosomal dominance. Allergic rhinitis can also be caused by food antigens. One of the ways to find out which foods are causing allergic rhinitis is a provocation test. It can also be diagnosed by avoiding eating those foods. Q. What is a provocative test
A. In diagnosing food allergen-induced allergic rhinitis, it is also diagnosed with a provocation test. Do not eat any food suspected to cause allergic rhinitis for 2 to 4 weeks, and carefully observe whether the symptoms of allergic rhinitis improve, disappear, increase, or change while the food is not eaten for 2 to 4 weeks. At this time, if the symptoms of allergic rhinitis are significantly improved, you can think that there is a high possibility that the food caused allergic rhinitis. However, a diagnosis cannot be made definitively in this way. Then, if the symptoms of allergic rhinitis reappear almost as before when you eat the food that was suspected to have caused allergic rhinitis, it is highly probable that the food caused allergic rhinitis.
A method of diagnosing allergic diseases by finding the food (antigen) that caused allergic rhinitis in this way is called a challenge test (challenge test). Provocation testing should never be done at any time and should never be done at the will of the parent or patient. Even when allergic rhinitis is mild, your doctor may order a provocative test.
Q. Can I do a provocation test (challenge test) when I suspect that allergic rhinitis is caused by an antigen such as house dust or house dust mites?
A. You can do it. When children with allergic rhinitis caused by antigens such as house dust or house dust mites are in a house with a lot of house dust or house dust mites, symptoms of allergic rhinitis may appear with itchy nose and sneezing a lot. When symptoms of allergic rhinitis appear in this way, it can be suspected that allergic rhinitis is caused by house dust or house dust mite antigen. More often than not, a skin allergy test finds an antigen rather than a challenge test.
Q. What clinical tests are used to diagnose allergic rhinitis?
A. IgE blood test, nasal mucus test, allergy skin test, blood eosinophil test, Radioallergen Absorption Immunoassay (RAST), fiber optic parenteral examination, intranasal provocation test, Intranasal air flow test, nasal endoscopy Allergic rhinitis can be diagnosed with a blood flow test in the nasal mucosa. In general, the Department of Pediatrics does not diagnose allergic rhinitis, but rather diagnoses allergic rhinitis based on the presence or absence of symptomatic signs of allergic rhinitis and examination findings.
Q. Please explain about environmental control treatment and antigen avoidance treatment.
A. Allergens or triggers that can cause allergies are avoided or eliminated as far as possible. It is an ideal treatment method. More specifically: Allergens that can trigger allergic rhinitis or other types of allergic diseases – foods that can cause allergic rhinitis or other types of allergic diseases should be avoided as much as possible. Allergic rhinitis by breastfeeding or feeding hypoallergenic artificial nutrition to newborns or infants born to siblings of biological parents with allergic diseases or atopic constitution, if possible, instead of feeding artificial nutrition containing milk, milk protein, or soy protein. Prevents this from occurring and properly treats allergic rhinitis that has already occurred. In order to prevent allergic rhinitis and other allergic diseases, you should avoid eating other foods that are likely to trigger allergic diseases as much as possible. In particular, foods such as milk, eggs, and chocolate are well known as foods that can cause allergic rhinitis and other types of allergic diseases. Avoid such foods as much as possible. Occasionally, cravings for foods that cause allergic rhinitis may occur, so be careful. It is recommended to keep pets such as dogs, cats, and birds out of the house if possible and avoid contact with them. Inevitably, when keeping pets in the house, avoid contact with or inhalation of animal fur, saliva, dander, feathers, etc., and bathe the dog frequently. Plants and trees should not be raised in the house where children with the atopic constitution or allergic rhinitis live. Mold and mold grow in damp places such as basements, so adjust the humidity in your home appropriately to prevent mold or mold from growing. It is better to have a carpet that can be harvested and washed frequently, or not carpeted, as a fixed carpet can collect more house dust and allow house dust mites to grow better. Curtains should be washed frequently. Keep the house clean of house dust and prevent dust mites from growing. Children with allergic rhinitis or atopic constitution should not place anything other than bedding in the bedroom. Cover the bed mattress and spring box with plastic covers to keep dust mites from growing. In spring, when flowers are in full bloom, close the windows tightly to prevent pollen and mold from entering the house. When planting or mowing plants, pollen or mold can be inhaled into the airways, which can cause allergic rhinitis, allergic conjunctivitis, or bronchial asthma. It is difficult to absolutely avoid such antigenic contact but avoid contact as much as possible. You will need to wear a mask, wear glasses to prevent dust from entering your eyes, and mow the lawn as needed. During the ragweed flowering season, avoid going to areas where ragweed weeds grow. Never wear clothes made from animal or bird feathers, and never use feathers or fur on pillows or blankets. Reduce house dust mites and more with HEPA air filters or Acaricides. Kills cockroaches.
Q. I want to know about drug treatment for allergic rhinitis
A. Antihistamines There are first-generation antihistamines and second-generation antihistamines. anti-inflammatory treatment, antigen immunotherapy Treatment with Leukotriene receptor antagonists. Treatment with corticosteroids. Mast cell (master cell) stabilizer treatment. Treatment of nasal mucosal decongestants placed directly into the nasal cavity. Alpha-adrenergic agonist therapy. Combination treatment.
Q. Please tell us about the antihistamines used to treat allergic rhinitis.
A. Antihistamines are drugs used to treat allergic diseases by blocking the binding of histamine from mast cells (master cells) and basophils to cellular receptacles, collectively called antihistamines. Antihistamines are divided into first-generation antihistamines and second-generation antihistamines. Antihistamines such as Periactin, Chlor-trimeton, Benadryl, and Pyribenzamine are first-generation antihistamines. Only one type of first-generation antihistamine can be used to treat allergic rhinitis. When treated with first-generation antihistamines, it has a therapeutic effect on allergic rhinitis and also has a sedative and sleeping effect, so various side effects such as drowsiness may occur. So, these days, allergic rhinitis is mainly treated with second-generation antihistamines. Claritin, Astemizole, Cetirizine, Fexofenadine, Loratadine and others are second-generation antihistamines. When treating allergic rhinitis with second-generation antihistamines, the therapeutic effect is good, the sedative effect is small, and side effects such as drowsiness symptoms may appear. When allergic rhinitis is treated with antihistamines, the symptoms of runny nose, sneezing, itchy nose, and watery eyes are greatly improved. The disadvantage of the second-generation histamine treatment is that the nasal mucosal decongestant effect is very small. For that reason, there are ways to treat with a first-generation antihistamine before going to bed at night and a second-generation antihistamine during the day.
Q. Talk about anti-inflammatory medications used to treat allergic rhinitis
A. Antihistamines can treat allergic rhinitis by blocking the action of histamine. However, inflammation in the nasal passages is not treated. Anti-inflammatory drugs are used to treat such inflammation. Anti-inflammatory drugs include Budesonide, Fluticasone, Vancenase Aq Nasal Spray 0.084%, and Beclomethasone. Allergic rhinitis can be treated with a corticosteroid nasal spray, which is sprayed into the nasal mucosa
Q. Side effects of treatment with first-generation antihistamines
A. No matter what type of antihistamine is treated, side effects may occur during the treatment of allergic rhinitis with that antihistamine, and the side effects depend on the type of antihistamine. When treating allergic rhinitis or other allergic diseases with first-generation antihistamines, there may be side effects such as sleep, sedation, poor concentration, and side effects such as dry saliva. However, these side effects are less common when treated with second-generation antihistamines.
Q. When treating with antihistamines, do you treat with only one type of antihistamine?
A. When allergic rhinitis is treated with antihistamines, it can be treated well with one type of antihistamine. Sometimes, simultaneous treatment with two types of antihistamines is needed for better results. It is sometimes treated with antihistamines, nasal decongestants, and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Q. Can I develop resistance to treatment with one type of antihistamine?
A. There is. Depending on the symptoms and severity of allergic rhinitis, one or two of several types of first-generation antihistamines can be selected for treatment. When treating allergic rhinitis with first-generation antihistamines, the first-generation antihistamines no longer need to continue treatment according to the doctor’s instructions if the treatment effect is good for a while, but after a while the treatment effect is no longer visible There is. When treating allergic rhinitis with one type of antihistamine, if the treatment is good, you can continue with that drug as needed. Also, when treated with one type of antihistamine, the therapeutic effect is good for a while, but if you continue treatment with the same antihistamine for a long time, the therapeutic effect may gradually decrease, and then the therapeutic effect may disappear. Therefore, there are cases where the treatment is switched to another type of antihistamine. Q. What to consider when choosing an antihistamine for allergic rhinitis
A. Even when treating allergic rhinitis with antihistamines, it is ideal to select and treat an appropriate antihistamine according to the doctor’s diagnosis
Q. What are the typical second-generation antihistamines
A. Loratadine (Claritin), Cetirizine (Zyrtec), Fexofenadine (Allegra), and Desloratadine (Clarinex). Previously, these second-generation antihistamines could be treated with a doctor’s prescription, but Loratadine (Claritin) and Cetirizine (Zyrtec) can be purchased from a pharmacy without a doctor’s prescription. If you treat allergic rhinitis with a second-generation antihistamine, it is usually not treated with a first-generation antihistamine because the treatment effect is good and the side effects that make you sleep do not occur well.
Q. What are the side effects of second-generation antihistamines?
A. It has less sedation and very few side effects such as drowsiness. There is also a comprehensive treatment for allergic rhinitis made by combining the second-generation antihistamine and Sudafed, a nasal mucosal capillary decongestant.
Q. Can pseudoephedrine be used to treat allergic rhinitis?
A. of course. Sudafed is an alpha-adrenergic agonist. When you treat allergic rhinitis with Sudape, the symptoms of nasal congestion due to congestion of the nasal mucosa are greatly improved. These types of drugs are also called nasal mucosal decongestants. Nasal mucosal decongestants include oral tablets (tablets) and liquid potions, sprays that can be sprayed directly into the nasal passages, and nasal drops that can be dropped into the nasal passages. Some drugs contain only the ingredients of nasal mucosal decongestants, and there are comprehensive nasal mucosal decongestants made by mixing antihistamines and nasal mucosal decongestants. Oral pseudoephedrine, commonly used these days, is a type of nasal mucosal decongestant and does not contain an antihistamine. When treated with that drug, there is no pharmacological action of the antihistamine, only the decongestant action of the nasal mucosa. Nasal mucosal decongestants such as oral pseudoephedrine temporarily forcibly contract the mucosal capillaries in the nasal passages to reduce runny nose and temporarily relieve congestion in the nasal mucosal layers to greatly open the nasal passages. Allergic rhinitis can be treated with Sudafed, or it can be treated with a combination of antihistamines and Sudafed.
Q. Are there any comprehensive allergic rhinitis medications that can be used to treat allergic rhinitis?
A. of course. It can be treated with a combination of first-generation antihistamines and alpha-adrenergic agonists. Periactin, Chlor-triton, Benadryl, Pyribenzamine is a first-generation antihistamine, and you can choose only one first-generation antihistamine to treat allergic rhinitis, and it contains a first-generation antihistamine and nasal mucosal decongestant. Select one of the comprehensive drugs for allergic rhinitis treatment such as Rondec, Actifed, Naldecon, Novafed, Triaminic, and Dimetapp to treat allergic rhinitis can be treated. This “allergy drug” used to treat allergic rhinitis may contain only one type of antihistamine, and may contain both an antihistamine and a nasal mucosal decongestant.
Q. Can a cold be treated with a comprehensive drug for allergic rhinitis that is used to treat allergic rhinitis?
A. of course. This type of allergic rhinitis treatment is sometimes used to treat the symptoms of a cold, even when you have a cold to relieve the symptoms of the cold. It is important to note that when treating allergic rhinitis or a cold with these drugs, you must follow the doctor’s prescription. In particular, children under 2 years of age should not be treated for a cold with this type of allergic rhinitis drug, which is a comprehensive allergic rhinitis drug. Q. Regarding the nasal mucosal decongestant that is put directly into the nasal passages used to treat allergic rhinitis
A. It can be treated with nasal mucosal decongestants that are placed directly into the nasal passages. Afrin/oxymetazoline nasal suppositories or neo synephrine nasal contraceptives have the effect of relieving congestion in the nasal mucosa. Nasal drops (nasal drops) can be dropped into the nasal passages or sprayed into the nasal passages to relieve congestion in the nasal mucosa and quickly clear the nasal passages blocked by allergic rhinitis. Neosynephrine has a nasal spray and a nasal drop. Aprinze also has a nasal spray. Treatment by dropping nasal drops directly onto the nasal mucosa or treatment with nasal sprays can provide quick and temporary relief of mucosal congestion in the nasal passages. Depending on the type of drug, the nasal mucosal decongestion effect may last 6 to 12 hours, and the symptoms of blocked nose due to allergic rhinitis may temporarily improve. Continued treatment with these drugs for more than 5 days may damage the nasal mucosa. therefore When Aprin is treated with nasal mucosal decongestants such as nasal spray or neosynephrine nasal spray, it must be used according to the doctor’s prescription. You can buy these drugs at pharmacies without a doctor’s prescription.
Q. What kind of mast cell stabilizer is used to treat allergic rhinitis?
A. The mast cell stabilizer is sprayed directly into the nasal cavity to prevent the release of histamine granules in the mast cells. Cromolyn nasal spray is a mast cell stabilizer and has a pharmacological action that prevents the release of histamine granules from the mast cells. Cromolyn nasal spray is used to prevent bronchial asthma from triggering. Cromolyn nasal spray sprayed into the nasal passages can prevent allergic rhinitis from triggering and treat pre-existing allergic rhinitis. Cromolyn spray is sprayed into the nasal cavity for easy treatment and good prevention. Prophylaxis continues to be good even after weeks or months of continued use of Cromolynspray. Side effects of cromolyn injections are very rare. It can be purchased without a prescription, but its high cost is a major drawback.
Q. About corticosteroids used to treat allergic rhinitis
A. Corticosteroid Boommu is an anti-inflammatory or anti-inflammatory drug. The current trend is to treat mild allergic rhinitis with a second-generation antihistamine first, and to treat moderate allergic rhinitis or severe allergic rhinitis first with a corticosteroid nasal spray. Corticosteroid nasal sprays such as Beclomethasone, Budesonide, and Triamcinolone are sometimes used to treat allergic rhinitis by spraying them directly into the nasal passages. Beclomethasone nasal spray or beclomethasone nasal spray is available in two forms: a powder spray that can be sprayed into the nasal passages, and a liquid spray. Certain types of corticosteroid nasal sprays are treated by spraying them into both nasal passages 1 to 2 times a day as prescribed by your doctor. Depending on the course of treatment, allergic rhinitis may be treated for several weeks or months. In general, when treating allergic rhinitis with a corticosteroid nasal spray sprayed into the nasal cavity, the therapeutic effect usually starts to appear about 12 hours after the start of treatment. Side effects such as nasal bleeding, increased intraocular pressure, glaucoma, and delayed kidney growth may occur, but these side effects are usually rare after several weeks of treatment. In particular, when treating allergic rhinitis with corticosteroid nasal spray, you must use the drug according to your doctor’s prescription.
Q. Can corticosteroid injections treat allergic rhinitis?
A. When severe allergic rhinitis is not treated with other types of treatment, it can be treated with oral corticosteroids or intramuscular depot corticosteroids for several days.
Q. Can it be treated with leukotriene receptor antagonists?
A. It can be treated with leukotriene-receptor antagonists. Treatment with nasal Montelukast sodium (Singulair) can definitely improve symptoms of allergic rhinitis. These days, treatment with leukotriene receptor antagonists has a tendency to attempt suicide, which is being investigated.
Q. Is it treated with anticholinergics?
A. It can be treated with anticholinergics. Ipratropium bromide (Nasal Atrovent 0.03%) nasal spray can be sprayed into the nasal passages to treat allergic rhinitis. When you have a lot of clear runny nose, treatment with this type of drug is effective.
Q. Can antihistamines and nasal corticosteroids be used at the same time?
A. You can. It can be treated simultaneously with antihistamines and corticosteroids. For severe allergic rhinitis that cannot be treated well with oral antihistamines or corticosteroid nasal sprays, simultaneous treatment with oral antihistamines and corticosteroid nasal sprays can be very effective.
Q. In what cases can antigen immunotherapy be treated?
A. Moderate allergic rhinitis or severe allergic rhinitis that is not well treated with appropriate treatment Severe allergic rhinitis requiring treatment with systemic corticosteroids Severe allergic rhinitis that cannot be cured even with adequate treatment with appropriate corticosteroids Allergic rhinitis can be treated with antigen immunotherapy when sinusitis and or bronchial asthma and allergic rhinitis coexist.
Q. Please tell me about antigen immunotherapy
A. Pure antigenic substances can be purified and extracted from cat or dog hair or dander, pollen from plants, or house dust mites, which can cause allergic rhinitis. When the various types of antigen substances extracted in this way are contacted or injected into the skin layer of children with allergic rhinitis or other allergic diseases, the degree of skin reaction that appears when the child has an allergic disease is determined by what kind of antigen. You can find out if it’s caused by this. Antigen immunotherapy can be treated by subcutaneous injection of a very small amount of an antigenic substance found in the results of a skin test tested in children with allergic rhinitis. At first, immunotherapy is started with a minimal amount of antigenic substance, and the dose is gradually increased to the antigen-immunotherapy maintenance dose. After increasing up to the maintenance dose of antigen immunotherapy, it is normal to administer antigen immunotherapy by giving the maintenance dose every 2 to 6 weeks. It is said that the symptoms of allergic rhinitis are reduced by one-third when treated with such antigen immunotherapy. Antigen immunotherapy is a method of treating allergic rhinitis with antigens in this way. Antigen immunotherapy appears to be the ideal treatment for allergic rhinitis in theory, but it is not the first choice treatment for a number of reasons when treating allergic rhinitis. As described before, the symptoms of allergic rhinitis are not cured well or the symptoms of allergic rhinitis are not well treated, or the symptoms become severe, making it difficult to sleep even when properly treated by avoiding or removing allergens (antigens), allergy treatment drugs, and/or antigen removal and avoidance It is common to treat allergic rhinitis with antigen-immunotherapy when studying at school or at home is disrupted or daily life is greatly disrupted. Allergic rhinitis in infants and children before the age of 3 years is not usually treated with antigen-immunotherapy. Another study found that children in the 4 to a 14-year-old age group who were treated for allergic rhinitis with antigen-immunotherapy were significantly less likely to develop bronchial asthma. Treatment with antigen-immunotherapy can cause systemic side effects in 5 to 10% of cases, and some can be life-threatening. Another disadvantage is that the cost of treatment is also high. Antigen immunotherapy is usually administered by subcutaneous injection, but in the West, antigen immunotherapy is also performed by putting an antigen under the tongue.
Q. Results of treatment with corticosteroids and second-generation antihistamines
A. Severe allergic rhinitis can be treated with corticosteroid nasal spray and second-generation antihistamines, which have very little nasal sedative effect, and the treatment effect is very good. 36-80% of seasonal allergic rhinitis or 55-86% of perennial allergic rhinitis are well treated.
Q. What is Coblation turbinate reduction treatment? A. With chronic allergic rhinitis, the nasal mucosa can become congested and the nasal passages can become swollen and blocked. Allergic rhinitis or other causes can cause irritation, inflammation, and enlargement of the turbinate. The surgical treatment method to reduce the swollen and inflamed turbinate volume without damaging the nasal mucosal tissue is the cobration turbinate alleviation treatment. If you have a stuffy nose and all medical treatments don’t work, you can try this method (source-Pediatric News, July 2007).
Q. I’ve heard in the news recently that the age at which allergic rhinitis starts depends on the trigger. explain about him?
A. The age at which allergic rhinitis begins depends on the triggering factor. Suffering from allergic rhinitis is also a problem, and the cost of treatment is also considerable. And children with allergic rhinitis are more prone to sinusitis, nasal polyps, otitis media, sleep problems, and bronchial asthma. Milk, eggs, flour foods, cockroaches, cats, dogs and house dust mites are “well known” as triggers of allergic rhinitis. Various health problems can appear due to sleep disturbance, apnea, lack of concentration, study difficulties, and decreased productivity. Allergic rhinitis can develop before the age of 1 year, but true allergic rhinitis rarely develops before 1 year of age. Since IgE antibodies, which play a major role in causing allergic rhinitis, appear later than IgG, IgA, and IgM antibodies, allergic rhinitis is less likely to develop before 1 year of age. Because pollen-induced allergic rhinitis takes about three years after exposure to pollen, it is not common for pollen allergic rhinitis to develop before the age of 3 years. Perennial rhinitis caused by house dust mites (allergic rhinitis with symptoms all year round) rarely develops before age 9. Allergic rhinitis caused by milk or milk-based foods accounts for about 0.3%. The incidence of allergic rhinitis in children with atopic constitution will be higher. Bronchial asthma may also develop in 50% of infants under 2 years of age with allergic rhinitis. However, it will occur at a much higher frequency than that. Fexofenadine (Allegra), Loratadine (Claritin), and Cetirizine (Zyrtec) are non-sedative histamines and do not provide sedation during treatment with this drug. Azelastine (Astelin) is a drug that has antihistamine and anti-inflammatory properties and is sprayed into the nasal cavity for treatment. Corticosteroids, such as Beclomethasone, Budesonide (RhinocortAqua), Dexamethasone, Flunisolide, Fluticasone Propionate, Mometasone Furoate, and Triamcinolone Acetonide, are nasal sprays for the treatment of allergic rhinitis. These corticosteroids have anti-inflammatory properties. These are topical allergic rhinitis medications used to treat allergic rhinitis by spraying intranasally. Atrovent nasal spray is a nasal capillary decongestant. Cromolyn sodium nasal spray has anti-inflammatory (anti-inflammatory) properties. Depending on the age and severity of allergic rhinitis, treatment of allergic rhinitis by selecting one or two of the above drugs is very effective. Severe allergic rhinitis can be treated with a corticosteroid nasal spray sprayed into the nasal passages and a second-generation antihistamine with minimal nasal sedative effect. 36-80% of seasonal allergic rhinitis and 55-86% of perennial allergic rhinitis are cured well. For more information on Budesonide nasal spray, please visit www.rhinocortaqua.com.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy of Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제1권 소아청소년 응급 의료
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제2권 소아청소년 예방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제3권 소아청소년 성장 발육 육아
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제4권 모유,모유수유, 이유
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유식, 비타민, 미네랄, 단백질, 탄수화물, 지방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제16권. 소아청소년 정형외과 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제17권. 소아청소년 피부 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제18권. 소아청소년 이비인후(귀 코 인두 후두) 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제19권. 소아청소년 안과 (눈)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제20권 소아청소년 이 (치아)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제21권 소아청소년 가정 학교 간호
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제22권 아들 딸 이렇게 사랑해 키우세요
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제23권 사춘기 아이들의 성장 발육 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제24권 소아청소년 성교육
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제25권 임신, 분만, 출산, 신생아 돌보기
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th- 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
- 응급환자관리 정담미디어
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- 소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
- The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
- Neonatology Jeffrey J. Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
- Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- 임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
- Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
- Sources and references on Growth, Development, Cares, and Diseases of Newborn Infants
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
- Emergency care, Harvey Grant and Robert Murray
- Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
- Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
- Neonatal resuscitation Ameican academy of pediatrics
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A.
- 제4권 모유, 모유수유, 이유 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유, 비타민, 단백질, 지방 탄수 화물 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제6권 신생아 성장발육 양호 질병 참조문헌 및 출처
- 소아과학 대한교과서
-
제18권 소아청소년 이비인후과 질환 참조문헌 및 출처
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Gray’s Anatomy
-
Habilitation of The handicapped Child, The Pediatric Clinics of North America, Robert H Haslam, MD.,
-
Pediatric Otolaryngology Sylvan Stool
-
Hearing Loss In children, The Pediatric Clinics of North America Nancy Roizen,MD and Allan O Diefendorf, PhD
-
Recent Advances in Pediatric otolaryngology The Pediatric Clinics of North America
-
Pediatric Otolaryngology. The Pediatric Clinics of North America, David Tunkel, MD., Kenneth MD Grundfast, MD
Copyright ⓒ 2014 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
“Parental education is the best medicine.