편도와 편도 비대(편도선과 편도선 비대),Tonsils and tonsillar hypertrophy, 소아 편도 절재 수술. pediatric tonsillectomy
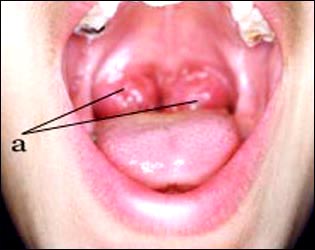
사진 147. a-비정상적으로 비대 된 양쪽 편도.
편도염으로 편도가 곪고 비대 됐다. 자녀의 입을 벌리게 하고 전등 빛을 비추어 자녀의 편도의 크기가 얼마나 큰지 꼭 진찰해보세요.
Copyright ⓒ 2001 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
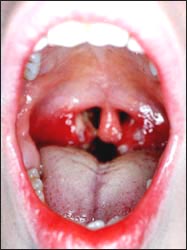
사진 148. 편도가 A군 베타 용혈성 연쇄상 연구균 감염으로 비정상적으로 비대 됐다.
Copyrigh tⓒ 2001 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
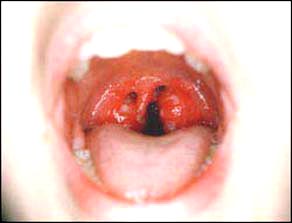
사진146. 편도 비대와 급성 박테리아 편도염.
급성 A 군 베타 연쇄상 구균에 의한 편도염이 생겼고 편도가 붓고 빯갛게 부었다
Copyright ⓒ 2001 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
- 전에 흔히 말하던 편도선을 요즘 편도(Tonsil)라고 한다.
- 편도는 구개편도, 인두편도, 설편도 등 여러 종류가 있다.
- 여기서는 인두 편도를 편의상 그냥 편도 또는 편도선이라 한다.
- 편도는 일종의 림프절이며 인두의 좌우에 한 개 모두 두 개가 있다.
- 편도는 경구를 통해 상 하기도나 위장관 속으로 들어오는 바이러스나 박테리아 또는 그 밖의 다른 병원체, 또는 비강을 통해 입안, 인두강 속, 기도 속, 위장관으로 들어온 바이러스나 박테리아, 또는 그 밖의 다른 병원체를 잡아 죽이는 역할도 하고
- 우리 몸에 해로운 항원이 입이나 콧구멍 속을 통해 몸속으로 침입할 때 편도는 그것들을 잡아서 인두 강 이상 더 깊숙이 신체의 다른 계통의 기관이나 조직으로 들어가지 못하도록 하는 방어 역할를 하고 면역체를 만드는 역할도 한다.
- 이런 이유 때문에 여러 종류의 박테리아나 바이러스 등이 인두, 또는 편도에 침입할 때 인두염 및, 또는 편도염 또는 인두편도염이 생길 수 있고, 또 아데노이드, 인두, 편도와 편도도 붓고 커진다.
- 입을 크게 벌리고 인두 강, 편도 등을 진찰할 때 신생아들이나 영아들의 편도는 육안으로 쉽게 볼 수 있을 정도로 그렇게 크지 않는 것이 보통이다.
- 출생 이후부터 영유아들이 점점 더 나이 먹음에 따라 몸이 커지는 것에 비례해서 편도의 크기도 점차로 더 커지고 생후 5~6세 유아들의 편도의 크기는 그들의 체중의 크기에 비례해서 일생동안 최고로 커지는 것이 보통이다.
- 그 생후 5~6세 이후 체중이 점점 더 커지고 편도도 점점 더 커지지만 편도가 커지는 속도는 체중이 커지는 속도만큼 더 이상 커지지 않는다.
- 이런 식으로 12~13세까지 서서히 조금씩 더 커지다가 그 이후부터는 더 이상 커지지 않고 그 크기대로 일 생동안 있는 것이 정상 편도성장과정이다.
- 그래서 12~13세 경 사춘기 아이들의 편도의 크기가 성인들의 편도의 크기와 거의 비슷하다.
- 즉, 12~13세 이후 사춘기 아이들의 편도의 크기는 12~13세 사춘기 아이들의 편도의 크기에 비해 별 변화가 생기지 않는 것이 보통이다.
- 다시 말하면 12~13세 때의 편도의 크기는 성인이 되었을 때의 편도 크기와 거의 같다. 즉 12~13세 이후 편도의 크기는 거의 같은 것이 정상적이다.
- 사춘기 때부터 성인이 되기까지 목안은 계속 조금씩 더 커지지만 편도의 크기는 더 이상 계속 커지지 않기 때문에 사춘기 이후 편도의 크기가 목안의 크기에 비해 작게 보인다.
- 바이러스 상기도 염을 앓을 때 바이러스성 감염이 비강, 인두, 편도 등에 동시 함께 생기고 그로 인해 편도가 붓고 더 커지는 것이 보통이다.
- 알레르기 비염이나 기관지 천식, 또는 아토피성 피부염 등 알레르기 질환의 병력이 있는 아이들이나 아토피성 체질이 있는 아이들의 편도의 크기는 그렇지 않는 아이들의 편도의 크기에 비해 항상 더 커져 있는 것이 보통이다.
- 편도가 편도 점막층 표면 위로 솟아 나와 있는 정도에 따라, 또 점막층 표면 위로 어느 정도로 많이 솟아나와 있느냐, 점막층 아래로 어느 정도 묻혀 있는냐에 따라 정상 편도의 크기가 많이 다르다( 알레르기 비염 참조).
- 어떤 편도는 인두 강 기도 부분의 전체를 다 차지할 수 있을 정도로 비정상적으로 상당히 커서 있고 숨 쉬는 데도 지장이 생길 수 있다(사진 147 참조).
- 경우에 따라 편도와 아데노이드의 크기가 비정상적으로 상당히 커지고 그에 따라 심장도 커질 수 있다.
- 편도가 비정상적으로 상당히 커져 있을 때는 아데노이드도 비정상적으로 커지는 것이 보통이고, 턱 바로 밑에 있는 목 림프절도 비정상적으로 상당히 커져 있는 경우가 많다.
|
다음은 “편도수술(Tonsillectomy), 수면 무호흡증, 폐쇄성 수면 무호홉증 ”에 관한 인터넷 소아청소년 건강상담 질의응답의 예 입니다. |
Q&A. 편도수술(Tonsillectomy), 수면 무호흡증, 폐쇄성 수면 무호홉증
Q.
- 5세 남아인데, 아주 어릴 때부터 감기에 자주 걸리고, 또 아토피입니다.
- 작년 가을부터는 감기만 걸리면 중이염이 오고, 계속 재발했습니다.
- 특히, 겨울철에는 내내 약을 달고 살고, 항생제를 많이 복용한 것도 신경이 쓰입니다. 작년에 안 사실인데, 편도도 크고, 아데노이드도 크다고 하더군요. 항상 입을 벌리고 있고, 잘 때 코도 고는 편입니다.
- 항상 피로를 잘 느끼고, 그래도 밤에는 코 고는 애치고는 잘 자는 편입니다. 근데, 간혹 자다일어나 앉아있다 자거나, 드렁 하면서 놀라 일어날 때도 있습니다. 특히 낮잠 잘 때 많이 울거나, 잘 놀다가도 어느 순간에 스르르 자버립니다. 5세가 되면 낮잠을 안 재워도 충분히 견디던데. 우리 애는 오후 3시 정도가 되면 정신을 못 차릴 정도로 졸려하고, 그 시간에는 외출도 못 할 정도입니다. 저녁에 일찍 자도 항상 졸려하는 건 마찬가지더라구요. 그게 잠이 많아서 그런 건지, 아데노이드가 큰 것과 연관이 있는 건지. 그리고 발음도 웅얼웅얼 정확하지 않습니다.
- 작년부터는 잘 크지도 않고, 편식도 있고, 아무튼, 소아청소년과 선생님으로부터 편도 수술을 고려해 보라는 얘기를 들었는데, 어떻게 해야 할지 잘 모르겠습니다. 글이 많이 길어졌는데, 상담 부탁드립니다.
A.
진주님께
안녕하세요. 질문해 주셔 감사합니다. 자녀의 나이, 성별, 과거와 가족의 병력, 진찰소견, 임상검사 결과 등 많은 정보가 있으면 더 좋은 답변을 드릴 수 있습니다. 주신 정보를 토대로 답변을 드립니다.
소아과 교과서에 있는 아토피성 체질, 만성 알레르기 비염, 기관지 천식, 폐쇄성(차단성) 수면 무호흡증, 긴장성 피로 증후군, 행동과증(행동과다증)과 집중력 결여증(주의력 결핍장애), 수면 부족, 코골이, 아데노이드 비대, 편도 비대, 구강 호흡(경구호흡) 등의 알레르기의 증상 징후들을 너무도 정확하게 모아 주셨습니다.
알레르기 비염, 아데노이드 비대, 편도 비대, 코골이, 폐쇄성 수면 무호흡증, 수면 곤란, 집중력 결여증 등이 자녀에게 있는 것 같습니다.
Q.
아주 어릴 때부터 감기에 자주 걸리고 아토피입니다.
A.
아토피성 체절이 있는 소아 청소년들은 감기에도 더 잘 걸립니다. 또 감기에 걸리면 감기로 천식발작이 유발될 수 있습니다.
자녀의 경우, 감기를 앓을 때 감기로 천식 발작이 유발되어 천식을 앓았던 것 같습니다.
수면 유발성 천식이 생겨 밤에 기침하고 호흡곤란이 있으면 천식 치료약으로 천식을 치료하면 증상이 좋아질 겁니다.
Q.
작년 가을부터는 감기만 걸리면 중이염이 오고, 계속 재발했습니다.
A.
[부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제 18권 소아 청소년 이비인후 질환– 급성 중이염, 재발성 중이염, 삼출성 중이염”을 참고 하 하시면 많이 도움 될 것입니다.
아토피성 체질이 있는 아이들은 알레르기 비염도 앓을 수 있고 이관이 막히고 중이염에 잘 걸립니다.
Q.
작년에 안 사실인데, 편도도 크고, 아데노이드도 크다고 하더군요. 항상 입을 벌리고 있고, 잘 때 코도 고는 편입니다.
A.
알러젠(항원)이 입과 코를 통해 인두 강과 인두 강 이상 몸 안 깊숙이 들어온다, 때문에 코로 들어오는 알러젠을 아데노이드가 책임지고 잡아 처리 합니다.
신체 다른 계통을 통해 들어오지 못하고 입을 통해 인두 강으로 들어오는 알러젠은 구개 편도, 인두 편도 설편도 등이 책임지고 잡아 더 이상 신체 내 다른 계통으로 들어가지 못 하게 일을 한다. 그렇게 일을 열심히 일 하다 보면 아데노이드와 편도가 비대되고 아데노이드 비대로 비강 기도 부분이 막히면 입으로 숨 쉬게 되어 입을 항상 벌리게 되는 것입니다.
Q.
항상 피로를 잘 느끼고,
A.
상기도 기도 부분이 일부 막혀 산소 섭취량이 적어지고 잠도 제대로 자지 못하고 그 외 다른 이유로 아토피성 체질인 아이들은 피로를 더 많이 더 자주 느낍니다. 만성 피로증후군도 잘 생길 수 있습니다.
Q.
그래도 밤에는 코고는 애치고는 잘 자는 편입니다. 근데, 간혹 자다일어나 앉아있다 자거나, 드렁 하면서 놀라 일어날 때도 있습니다.
A.
알레르기 비염으로 비강 기도 부분이 막히고 아데노이드도 크고 편도도 커서 비인후의 해부학 구조변화가 생겨 코를 골게 됩니다.
때로는 숨길이 막히면 자다가 일어나게 됩니다.
이런 현상을 폐쇄성 수면 무호흡증이라 합니다.
상기도가 막혀 폐쇄성 수면 무호흡증이 생기면 자다가 깨기도 합니다.
Q.
특히 낮잠 잘 때 많이 울거나, 잘 놀다가도 어느 순간에 스르르 자버립니다.
5세가 되면 낮잠을 안 재워도 충분히 견디던데. 우리 애는 오후 3시 정도가 되면 정신을 못 차릴 정도로 졸려하고, 그 시간에는 외출도 못 할 정도입니다. 저녁에 일찍 자도 항상 졸려하는 건 마찬가지더라구요. 그게 잠이 많아서 그런 건지, 아데노이드가 큰 것과 연관이 있는 건지. 그리고 발음도 웅얼웅얼 정확하지 않습니다.
A.
관련이 있습니다. 이상 설명한 여러 가지 원인으로 상기도 기도 부분이 일부 막히면 잠을 푹신 잘 수 없어서 그럴 겁니다.
낮에는 정신을 집중을 못해 주의력 결핍장애(집중력 결여증)이 있는 아이들도 많이 있습니다. 그래서 학교에서 공부릏 잘 할 수 없습니다.
Q.
작년부터는 잘 크지도 않고, 편식도 있고,
A.
의식주, 건강, 사랑, 수면은 인간 삶의 기본 중 기본입니다.
잠을 제대로 자지 못해 정신도 없고, 집중도 못하고 음식물 맛도 없으니 성장도 잘못할 수 있습니다. 여러 가지 원인으로 성장 지연도 생길 수 있습니다.
Q.
아무튼, 소아청소년과 선생님으로부터 편도수술을 고려해 보라는 얘기를 들었는데, 어떻게 해야 할지 잘 모르겠습니다.
A.
- [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제 15권 소아 청소년 알레르기 및 면역질환을 전부 자세히 읽어 보세요.
- 특히 알레르기 질환의 예방, 알레르기 비염, 음식물 알레르기, 기관지 천식 등을 하나도 빼놓지 말고 읽어 보세요.
- 단골 소아청소년과 의사와 상의하시고 여기서 제시한 예방 치료에 동의하시면 당장 실시하세요.
- 제 18권 소아청소년 이비인후 질환–중이염,
- 아데노이드 비대와 편도 비대와 절제 수술.
- 제 17권 소아청소년 피부질환–아토피성 피부염,
- 폐쇄성 수면 무호흡증, 코골이, 아데노이드 비대와 편도 비대 등을 참조하시기 바랍니다.
- 거기에 좋은 정보가 많이 있습니다.
- 알레르기 질환을 잘 예방하고 치료를 잘 하면 그런 증상이 아주 좋아집니다.
- 낮에 한쪽 콧구멍을 한 손가락으로 끝으로 살짝 막고 입을 다물게 하고 다른 콧구멍을 통해 숨을 쉬어보라고 해보셔요.
- 비강이 아주 좁게 막혀 있을 겁니다.
- 저도 많이 걱정합니다.
- 적극적으로 치료해 주시고 알레르기를 예방해 주시면 많이 좋아질 겁니다.
- 소아청소년과에서 진단 치료를 계속 받으시고 이런 문제에 관해서 상담하시기 바랍니다.
- 치료가 잘 안 되면 이비인후과 전문의와 소아 알레르기 소아청소년 전문의의 도움을 받으시면 좋을 줄로 압니다.
- 질문이 더 있으시면 또 방문해 주십시오. 감사합니다. 이상원 드림
|
다음은 “코골이 편도 비대 추가 질문요 ”에 관한 인터넷 소아청소년 건강상담 질의응답의 예 입니다. |
Q&A. 코골이 편도 비대 추가 질문요
Q.
- 답변 감사합니다.
- 저희 아이는 지금 38개월 된 남자아이고 사는 곳이 이곳이 중국이라상담을 추가로 드립니다. 오늘 병원에 다녀왔는데 편도가 아주 심하게 부었고 염증은 없는 것으로 보인다고 합니다.
- 감기증상도 보이지 않고 있거든요 단지 의사선생님은 피곤해서(유치원 개학과 더불어) 그런 것 같다고 하시네요. 그리고 제가도가 자주 붓는 편인데 유전이며 편도가 비대하다고 하십니다. 그리고 딱히 약은 처방해 주시지 않았습니다.
- 근데 걱정은 코골이가 지속되고 있는 것과 편도가 계속적으로 부어 있는 것 같아 걱정입니다.
- 편히 휴식을 취하게 하는 것 외에 다른 방법이 있는지요. 그리고 지속적으로 편도로 인해 코를 골게 될까봐 걱정이네요
A.
정님
- 안녕하세요. 또 질문해 주셔 감사합니다. 자녀의 나이, 성별, 과거와 가족의 병력, 진찰소견, 임상검사 결과 등 많은 정보가 있으면 더 좋은 답변을 드릴 수 있습니다. 주신 정보를 참작해 답변을 드립니다.
- 여기는 미 동북부 보스턴에서 2시간, 뉴욕에서 2시간 반 그리고 미국 대학 농구 여자 남자팀이 작년에 최우승한 UCONN 대학교가 있는 조그마한 도시입니다.
- 인제 봄기운이 햇살을 통해서 살살 불어옵니다.
- 그러나 특별히도 우리 집 뒤뜰에는 3~4cm정도 눈이 많이 쌓여 있습니다. 거기는 중국 어디인가요.
- 제가 운영하는 “부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다-www.koreapediatrics.com.”은 부족한 점이 있지만 이용해 주셔 감사합니다.
- 의, 식, 주, 건강, 사랑, 잠은 자녀들이 건강하고 행복하게 자라는데 필요한 기본 필수품입니다. 소아청소년(0~18세)들을 육아 하는데 미국식 육아 법, 이스라엘 육아법, 한국식 육이법, 중국식 육아법이 따로 없습니다. 저의 “부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다-www.koreapediatrics.com.”은 전 세계 8천만 한인들을 위 한 건강 양육, 질병의 원인 증상 징후 진단 치료 예방에 관한 지침서입니다.
- 저녀를 양육하는 중 이용하셔 중국에 계신 한인 동포 여러분 그리고 이북을 비롯해 전 세계 한인들이 이용해서 자녀 양육하는 데 도움이 되면 좋겠습니까. 긴 말씀드린 것을 용서해 주십시오.
- 아이들의 편도가 보통보다 더 큰 원인은 몇 가지가 있습니다.
- 타고날 때부터 인두 강 내 편도 위치에 따라 입을 벌렸을 때 편도가 또래들의 편도의 크기보다 더 크게 보이는 경우가 있습니다. 즉 정상적인 크기의 편도가 좀 더 크게 보일 수 있습니다.
- 이것은 정상적인 것입니다.
- 바이러스 감염이나 A군 베타 용혈성 연쇄상구균 감염 등 병원체 감염이 편도에 생기면 편도가 비정상적으로 커지고 붓고 때로는 고름이 잡히고 상당히 더 커집니다.
- 이런 경우 목안이 아프고 열이 나고 인두가 아프고 인두 점막도 부며 붉게 변할 수 있습니다.
- 때로는 바이러스 감염으로 편도가 붓고 거기에 염증이 생기면 인두, 비강, 부비동 등에도 염증이 생깁니다.
- 거기다가 아데노이드에도 염증이 동시에 생길 수 있습니다.
- 이런 경우를 감기라고 진단을 부치기도 하고 인두편도염(Pharyngotonsillitis)이라고 진단 부치기도 합니다.
- 이 때 입을 크게 벌리면 커진 편도를 부모들도 육안으로 볼 수 있습니다. 이런 경우, 코도 골 수 있고 숨 쉬는 데 곤란이 생길 수 있습니다.
- 편도의 위치도 정상이고 편도에 바이러스 감염이나 세균 감염이 없는데도 타고날 때부터 아토피성 체질이나 코를 통해서 또는 입을 통해서 들어오는 알러젠(항원/Allergen)으로 코에 알레르기성 비염이 생기고 부비동염이 잘 생기고 아데노이드도 커지고 입안에 있는 편도도 비정상적으로 커지는 경우가 있습니다.
- 이 경우 알레르기 질환을 잘 치료하지 않고 환경 콘트롤을 잘 하지도 않고 알레르기 질병 유발 인자를 피하지도 않고 제거하지도 않으면 이런 현상이 계속되고 눈에도 알레르기가 생기고 눈이 자주 충혈 되고 붉어지고 눈물이 자주 나고 알레르기성 결막염이 생길 수 있습니다.
- 거기다가 아래 눈꺼풀 바로 밑 피부가 검푸르게 생깁니다. 이런 현상을 알러지 샤이너라고 합니다.
- 다시 코 문제로 돌아가서, 코가 자주 막히고 그로 인해서 입을 벌리고 숨 쉬는 때가 더 많이 있습니다.
- 보통 눈으로 볼 수 없지만 십중팔구는 아데노이드가 커져 있고 숨 쉬는 데 또한 곤란을 가집니다.
- 거기다가도 편도도 커집니다.
- 이런 경우 코로 숨쉬기가 더 곤란하고 입을 벌리고 숨을 쉬는 때가 더 많이 있습니다.
- 또 코를 골게 됩니다.
- 심함 경우는 수면 중 일시적 차단성 수면 무호흡증이 생깁니다.
- 때로는 턱 밑 목 앞에 있는 림프절도 커집니다.
- 이런 증상 징후들은 아주 경한 경우도 있고 심한 경우도 있습니다.
- 심할 때는 코를 골고 숨을 입으로 쉬는 증상 징후가 나타납니다.
- 알레르기 항원을 피하고 제거하고 알레르기 질환을 잘 치료해야 합니다.
- 특히 의사가 치료는 것도 중요하지만 부모들이나 환아 자신이 해야 할 치료 문제가 아주 많습니다.
- 때로는 부모들이 여러 면에서 더 희생을 해야 합니다. 필요에 따라 한 지방에서 다른 지방으로 이사 가서 살아야합니다.
- 부모의 직장도 바꿔야 하는 경우도 있습니다.
- 호흡기 알레르기 질환에 호흡기 감염병이 동시 있으면 그 감염병도 물론 치료해 주어야 합니다.
- 그 외 편도에 농양이나 종양이 생기거나 다른 이유로 편도가 커질 수 있습니다.
- 피로를 느끼는 원인은 많이 있습니다. 음식물 알레르기로 인한 피로할 수 있습니다.
- 아토피성 체질이 있는 아이들에게 긴장성 피로 증후군이 더 잘 생깁니다.
- 자녀의 경우 무엇 때문에 편도가 커졌는지 코를 고는지 인터넷을 통해서 확실히 다 말씀드릴 수 없으나 위의 설명을 참조하시고 무엇 때문에 편도가 커져 있는지 짐작하실 수 있을 것입니다.
- 그리고 의사와 상담하시면 진단이 나고 치료의 방향도 설 것입니다.
- 알레르기로 인한 편도 비대는 알레르기가 유전성이기 때문에 가족 중 다른 식구에게도 거의 같은 증상 징상이 생길 수 있습니다.
- [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제 2권 소아청소년 질병 안전사고 예방–알레르기 예방. 제 8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환–감기, 편도염. 제 15권 소아청소년 알레르기 및 면역질환–알레르기성 비염, 음식물 알레르기. 편도 비대, 아데노이드 비대, 코골이 등을 참조하시기 바랍니다. 질문이 더 있으면 또 방문하세요. 감사합니다. 이상원 드림
Update 10/2019, Pediatrics
Pediatric tonsillectomy
편도선을 수술로 떼어 내는 수술 치료를 편도선 수술리라고 하고 미국에서는 연간 500,000 편도수술을 한다. 15%의 편도수술은 15세 이하 아아들에게서 한다. 20여년 전에는 편도선염이 주 편독 선 수술 치료 원인었으나 요즈음은 차단성 수면 장애호흡, 차단성 수면 무호흡증 등이 주 편도선 수술 이유이다.
Update 10/2019, Pediatrics
pediatric tonsillectomy
The surgical treatment to remove the tonsils by surgery is called a tonsillectomy, and 500,000 tonsillectomies are performed annually in the United States.
15% of tonsillectomies are performed in children under 15 years of age. About 20 years ago, tonsillitis was the main cause of tonsillectomy surgery, but these days, the main reasons for t tonsillectomy surgery are blocked sleep disorder breathing and blocked sleep apnea.
Tonsils and tonsillar hypertrophy, Pediatric tonsillectomy

Photo 147. a – abnormally hypertrophied bilateral tonsils. My tonsils were swollen and enlarged due to tonsillitis. Be sure to check the size of your child’s tonsils by opening their mouths and shining a light on them. Copyright ⓒ 2001 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Picture 148. The tonsils were abnormally enlarged due to group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus infection. Copyrigh tⓒ 2001 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Picture 146. Tonsil hypertrophy and acute bacterial tonsillitis. Tonsillitis caused by acute group A beta streptococcus, swollen and reddened tonsils Copyright ⓒ 2001 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
• The tonsils that were commonly referred to in the past are now called tonsils.
• There are several types of tonsils, such as palatine tonsils, pharyngeal tonsils, and lingual tonsils.
• Herein, the pharyngeal tonsil is simply referred to as tonsil or tonsil for convenience.
• The tonsils are a kind of lymph node, and there are two of them, one on either side of the pharynx.
• The tonsils are used to trap and kill viruses, bacteria, or other pathogens that enter the upper respiratory tract or gastrointestinal tract orally, or enter the mouth, pharynx, airways, or gastrointestinal tract through the nasal passages. also play a role
• When antigens that are harmful to our body enter the body through the mouth or nostrils, the tonsils catch them and serve as a defense to prevent them from entering the organs or tissues of other body systems deeper than the pharyngeal cavity, and also play a role in building the immune system. do.
• For this reason, when various types of bacteria or viruses enter the pharynx or tonsils, pharyngitis and/or tonsillitis or pharyngotonsillitis may occur, and the adenoids, pharynx, tonsils and tonsils also become swollen and enlarged.
• When examining the pharyngeal cavity and tonsils with the mouth wide open, the tonsils of newborns and infants are usually not so large that they can be easily seen with the naked eye.
• From birth, as infants and young children get older, the tonsils gradually increase in size in proportion to body size, and the size of the tonsils in infants 5 to 6 years of age is usually at a lifetime maximum in proportion to the size of their body weight. .
• After the age of 5 or 6 years, weight increases and the tonsils grow larger, but the rate at which the tonsils grow does not increase as much as the weight increases.
• In this way, it gradually grows bigger until the age of 12 to 13, and after that, it does not grow any more and stays at that size for the rest of your life. This is the normal process of tonsil growth.
• So, the size of tonsils in adolescents around 12-13 years of age is almost the same as the tonsils in adults.
• In other words, the size of the tonsils of adolescent children after 12-13 years of age does not usually change much compared to the size of the tonsils of adolescent children aged 12-13 years.
• In other words, the size of the tonsils at 12-13 years of age is almost the same as the size of the tonsils as adults. In other words, it is normal for tonsils to be about the same size after the age of 12-13.
• From puberty to adulthood, the throat continues to grow little by little, but the size of the tonsils does not continue to grow any longer.
• When you have viral upper respiratory tract infection, it is common for a viral infection to co-occur in the nasal cavity, pharynx, and tonsils, causing the tonsils to become swollen and enlarged.
• The tonsils of children with a history of allergic diseases such as allergic rhinitis, bronchial asthma, or atopic dermatitis or children with atopic constitution are usually always larger than the tonsils of children who do not.
• The size of the normal tonsils differs greatly depending on the extent to which the tonsils protrude above the surface of the tonsil mucosa, and how much they protrude above the surface of the tonsils and how much they are buried under the mucosal layer (see Allergic Rhinitis).
• Some tonsils are abnormally large enough to occupy the entire pharyngeal airway, and breathing may be impaired (see photo 147).
• Occasionally, the tonsils and adenoids become abnormally and significantly enlarged, resulting in an enlarged heart.
• When the tonsils are abnormally large, the adenoids are also abnormally enlarged, and the neck lymph nodes just below the chin are also abnormally large in many cases.
The following is an example of a Q&A on health counseling for children and adolescents on the Internet about “tonsillectomy, sleep apnea, and obstructive sleep apnea.”
Q&A.
Tonsillectomy, sleep apnea, obstructive sleep apnea
Q.
• He is a 5-year-old boy, and he has often caught colds from a very young age and is also atopic.
• Since last fall, if you catch a cold, you have otitis media and it has continued to recur.
• Especially in the winter, I’m worried about living on medication and taking a lot of antibiotics. Last year, I didn’t know it, but they said the tonsils are large and the adenoids are large. I always keep my mouth open and I tend to snore when I sleep.
• I feel very tired all the time, but I tend to sleep well for snoring babies at night. However, there are times when I wake up from sleep, sit down and sleep, or wake up surprised while drooling. In particular, they cry a lot while taking a nap, or fall asleep at any moment even after playing well. By the age of 5, I was able to tolerate it even without taking a nap. My child is so sleepy that he can’t wake up around 3pm, and he can’t even go out at that time. Even if I go to bed early in the evening, I always feel sleepy. Maybe it’s because I sleep a lot, or maybe it has something to do with large adenoids. And the pronunciation is also not very accurate.
• Since last year, I’m not very big, I have a picky eater, and anyway, my pediatrician told me to consider tonsillectomy, but I’m not sure what to do. This article is very long, so please help. A. to pearl Good morning. Thank you for asking a question. We can give you a better answer if you have a lot of information such as your child’s age, gender, past and family medical history, examination findings, and clinical test results. We will respond based on the information you have provided. Atopic constitution, chronic allergic rhinitis, bronchial asthma, obstructive (obstructive) sleep apnea, tension fatigue syndrome, hyperactivity (hyperactivity) and lack of concentration (attention deficit disorder), sleep deprivation, snoring, You have collected the symptoms of allergy such as enlarged adenoids, enlarged tonsils, and mouth breathing (oral breathing) so accurately. Your child seems to have allergic rhinitis, enlarged adenoids, enlarged tonsils, snoring, obstructive sleep apnea, trouble sleeping, and lack of concentration.
Q.
From a very young age, I often catch colds and have atopy.
A.
Children and adolescents with atopic segmentation are also more susceptible to colds. Also, if you catch a cold, the cold can trigger an asthma attack. In your child’s case, it is likely that the cold triggered an asthma attack when he had a cold. If you have sleep-induced asthma and have coughing and shortness of breath at night, treating your asthma with asthma medications will improve your symptoms.
Q. Since last fall, whenever I catch a cold, I have an otitis media and it has continued to recur.
A. [Parents should also become anti-doctors-Children and Family Nursing Encyclopedia]-Volume 18 Children’s Adolescent Otolaryngology-Acute Otitis Media, Recurrent Otitis Media, Otitis Media with Exudative Reference” Children with atopic constitution can also suffer from allergic rhinitis and are prone to otitis media with blocked ear ducts.
Q. Last year, I didn’t know it, but they said the tonsils are large and the adenoids are large. I always keep my mouth open and I tend to snore when I sleep.
A. Allergens (antigens) enter the body through the mouth and nose, beyond the pharyngeal and pharyngeal cavities, so the adenoids are responsible for capturing and processing allergens entering the nose. Allergens that enter the pharyngeal cavity through the mouth and cannot enter the body through other systems are captured by the palatine tonsils, pharyngeal tonsils, and tongue tonsils, and work to prevent them from entering other systems in the body. If you work hard like that, the adenoids and tonsils become enlarged, and if the nasal airways are blocked by the enlarged adenoids, you breathe through your mouth and always open your mouth.
Q. I always feel tired,
A. Children with atopic constitution feel tired more often and more often because of partial blockage of the upper airway, resulting in reduced oxygen intake, poor sleep, and other reasons. Chronic fatigue syndrome may also occur.
Q. However, at night, I tend to sleep well for a snoring child. However, there are times when I wake up from sleep, sit down and sleep, or wake up surprised while drooling.
A. Due to allergic rhinitis, the nasal airways are blocked, the adenoids are large and the tonsils are large, so the anatomical structure of the nasopharynx is changed and snoring occurs. Sometimes, when you are short of breath, you wake up. This phenomenon is called obstructive sleep apnea. Obstructive sleep apnea occurs when the upper airway is blocked.
Q. In particular, they cry a lot while taking a nap, or fall asleep at any moment even after playing well. By the age of 5, I was able to tolerate it even without taking a nap. My child is so sleepy that he can’t wake up around 3pm, and he can’t even go out at that time. Even if I go to bed early in the evening, I always feel sleepy. Maybe it’s because I sleep a lot, or maybe it has something to do with large adenoids. And the pronunciation is also not very accurate.
A. It is related. If the upper airway part is partially blocked due to the various reasons described above, it may be because you cannot sleep well. Many children have Attention Deficit Disorder (DAD) due to difficulty concentrating during the day. So, I can’t do well in school.
Q. Since last year, I am not growing well, I have a picky eater
A. Food, shelter, health, love, and sleep are the basics of human life. You can’t sleep properly, so you can’t concentrate, you can’t concentrate, and you can’t taste food, so growth can go wrong. Growth retardation can also occur for a number of reasons.
Q. Anyway, I’ve been told by my pediatrician to consider a tonsillectomy, but I’m not sure what to do.
A.
www.drleepediatrics.com-Volume 15 Read all children and adolescent allergies and immune diseases in detail.
• In particular, do not miss out on the prevention of allergic diseases, allergic rhinitis, food allergy, and bronchial asthma.
• Consult with your regular pediatrician, and if you agree to the preventive treatment suggested here, do it right away.
• Volume 18 Children’s and Adolescent Otolaryngitis – Otitis Media,
• Hypertrophy of adenoids and enlarged tonsils and surgical resection.
• Vol. 17 Skin Diseases in Children and Adolescents – Atopic Dermatitis, • See obstructive sleep apnea, snoring, enlarged adenoids and enlarged tonsils, etc.
• There is a lot of good information there.
• Allergies can be greatly improved by preventing and treating them well.
• During the day, gently close one nostril with the tip of one finger, close your mouth and try to breathe through the other nostril.
• Your nasal passages will be very narrow.
• I worry a lot too.
• If you take active treatment and prevent allergies, you will feel much better.
• Continue to receive diagnostic treatment from the Department of Pediatrics and discuss these issues.
• If the treatment does not go well, I think it would be good to seek help from an otolaryngologist and a pediatric allergy specialist.
• If you have more questions, please come back. Thank you. Lee Sang-won.
The following is an example of an Internet pediatric health consultation Q&A regarding “Additional Questions for Snoring Tonsil Hypertrophy”.
Q&A. Snoring tonsil enlargement additional question
Q.
• Thank you for answer.
• My child is a 38-month-old boy and he lives in China, so we provide additional counseling. I went to the hospital today, and the tonsils are very swollen and there seems to be no inflammation.
• I don’t have any symptoms of a cold, so the doctor just said it was because I was tired (along with the opening of kindergarten). Also, I tend to swell often, but they say that it is hereditary and that the tonsils are enlarged. And he didn’t prescribe any medications.
• But I am concerned that snoring continues and the tonsils are constantly swollen.
• Is there any other way other than making it easy to rest? And I’m worried that I’m constantly snoring from the tonsils.
A. jung nim
• Good morning. Thank you again for asking. We can give you a better answer if you have a lot of information such as your child’s age, gender, past and family medical history, examination findings, and clinical test results. We will respond based on the information you have provided.
• This is a small town with two hours from Boston in the Northeast, two and a half hours from New York, and UCONN, where the men’s college basketball women’s team won the championship last year.
• Inje spring vibes are gently blowing through the sunlight.
• However, especially in the backyard of our house, there is a lot of snow about 3-4cm. Where is China?
• There are some shortcomings in “Parents should also become anti-doctors-www.koreapediatrics.com.” I run, but thank you for using it.
• Clothing, food, shelter, health, love, and sleep are basic necessities for children to grow up healthy and happy.
There are no American-style parenting laws, Israeli parenting laws, Korean-style parenting laws, or Chinese-style parenting laws for raising children (0-18 years old). My “Parents Should Be Anti-Doctors – www.koreapediatrics.com.” is a guide on health care, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of causes, symptoms, and signs of disease for 80 million Koreans around the world.
• Would you like to use it while raising a child, and help Korean Koreans in China and North Koreans around the world to raise their children by using it? Please forgive me for my long words.
• There are several reasons why children’s tonsils are larger than normal.
• Depending on the location of the tonsils in the pharyngeal cavity from birth, the tonsils may appear larger than the tonsils of their peers when they open their mouths. This means that a normal-sized tonsil may appear slightly larger.
• This is normal.
• When the tonsils are infected with a pathogen, such as a viral infection or a group A beta-hemolytic streptococcal infection, the tonsils become abnormally large, swollen, sometimes pus-filled, and significantly larger.
• In this case, you may have a sore throat, a fever, a sore throat, and the pharyngeal mucosa may also become swollen and red.
• Sometimes a viral infection causes the tonsils to become inflamed and inflamed, causing inflammation in the pharynx, nasal passages, and sinuses as well.
• In addition, the adenoids may become inflamed at the same time.
• This case is sometimes diagnosed as a cold or as Pharyngotonsillitis.
• Parents can see the enlarged tonsils by opening their mouths wide at this time. In this case, you may be able to snore and have trouble breathing.
• Even though the tonsils are in normal position and there is no viral or bacterial infection in the tonsils, allergic rhinitis occurs in the nose due to atopic constitution from birth, or an allergen (antigen) that enters through the nose or through the mouth, sinusitis, and adenoids In some cases, the tonsils in the mouth also become abnormally enlarged.
• In this case, if the allergic disease is not treated well, the environment is not well controlled, and the allergens are not avoided or eliminated, this phenomenon will continue, and the eyes will become allergic, and the eyes are often red, red, watery, and allergic. Conjunctivitis may develop.
• In addition, the skin just below the lower eyelid becomes dark blue. This phenomenon is called allergy shiner.
• Coming back to the nasal problem, my nose is often stuffy and that causes me to breathe more with my mouth open.
• Although usually invisible to the naked eye, in all cases they have enlarged adenoids and also have difficulty breathing.
• Plus, the tonsils get bigger.
• In this case, breathing through the nose is more difficult and breathing with the mouth open more often.
• You will snore again.
• In severe cases, transient obstructive sleep apnea occurs during sleep.
• Sometimes the lymph nodes in the front of the neck under the chin also enlarge.
• These symptoms can be very mild or severe.
• In severe cases, symptoms include snoring and breathing through the mouth.
• Avoid and eliminate allergens and treat allergens well.
• Although it is especially important for the doctor to treat you, there are many treatment problems that parents and children themselves have to deal with.
• Sometimes parents have to make more sacrifices in many ways. You have to move and live from one province to another as needed.
• Parents may also need to change jobs.
• If a respiratory allergic disease and a respiratory infectious disease are present at the same time, of course, the infectious disease must also be treated.
• Other tonsils can become enlarged, such as an abscess or tumor, or for other reasons.
• There are many causes of fatigue. Food allergies can cause fatigue.
• Children with the atopic constitution are more likely to develop tension fatigue syndrome.
• In the case of your child, it is not possible to say for sure what causes enlarged tonsils or snoring through the Internet, but you can get an idea of what causes enlarged tonsils by referring to the explanation above.
• And if you talk to your doctor, a diagnosis will be made and treatment will be established.
• Tonsil enlargement due to allergy, because the allergy is hereditary, other members of the family may have almost the same symptoms.
•www.drleepediatrics.com – Volume 2 Prevention of Safety Accidents in Children and Adolescents – Prevention of Allergy Book 8 Respiratory Diseases in Children and Adolescents – Colds and Tonsillitis. Book 15 Allergy and Immune Disorders in Children and Adolescents-Allergic Rhinitis and Food Allergy. See also tonsil hypertrophy, adenoid hypertrophy, snoring, etc. Please visit again if you have more questions. Thank you. Lee Sang-won.
Update 10/2019, Pediatrics
pediatric tonsillectomy
The surgical treatment to remove the tonsils by surgery is called a tonsillectomy, and 500,000 tonsillectomies are performed annually in the United States.
15% of tonsillectomies are performed in children under 15 years of age. About 20 years ago, tonsillitis was the main cause of tonsillectomy surgery, but these days, the main reasons for t tonsillectomy surgery are blocked sleep disorder breathing and blocked sleep apnea.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy of Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제1권 소아청소년 응급 의료
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제2권 소아청소년 예방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제3권 소아청소년 성장 발육 육아
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제4권 모유,모유수유, 이유
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유식, 비타민, 미네랄, 단백질, 탄수화물, 지방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제16권. 소아청소년 정형외과 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제17권. 소아청소년 피부 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제18권. 소아청소년 이비인후(귀 코 인두 후두) 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제19권. 소아청소년 안과 (눈)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제20권 소아청소년 이 (치아)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제21권 소아청소년 가정 학교 간호
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제22권 아들 딸 이렇게 사랑해 키우세요
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제23권 사춘기 아이들의 성장 발육 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제24권 소아청소년 성교육
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제25권 임신, 분만, 출산, 신생아 돌보기
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th- 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
- 응급환자관리 정담미디어
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- 소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
- The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
- Neonatology Jeffrey J. Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
- Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- 임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
- Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
- Sources and references on Growth, Development, Cares, and Diseases of Newborn Infants
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
- Emergency care, Harvey Grant and Robert Murray
- Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
- Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
- Neonatal resuscitation Ameican academy of pediatrics
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A.
- 제4권 모유, 모유수유, 이유 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유, 비타민, 단백질, 지방 탄수 화물 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제6권 신생아 성장발육 양호 질병 참조문헌 및 출처
- 소아과학 대한교과서
-
제18권 소아청소년 이비인후과 질환 참조문헌 및 출처
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Gray’s Anatomy
-
Habilitation of The handicapped Child, The Pediatric Clinics of North America, Robert H Haslam, MD.,
-
Pediatric Otolaryngology Sylvan Stool
-
Hearing Loss In children, The Pediatric Clinics of North America Nancy Roizen,MD and Allan O Diefendorf, PhD
-
Recent Advances in Pediatric otolaryngology The Pediatric Clinics of North America
-
Pediatric Otolaryngology. The Pediatric Clinics of North America, David Tunkel, MD., Kenneth MD Grundfast, MD
Copyright ⓒ 2014 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
“Parental education is the best medicine.