아데노이드 기능과 아데노이드 비대, Adenoids function and adenoidal hypertrophy
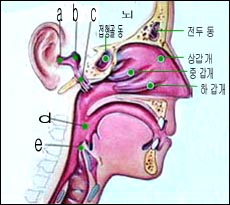
그림 150. 상· 하기도
a-귓구멍, b-중이, c-이관, d-인두, e-후두개
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD,. FAAP
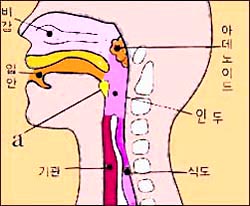
그림 151. 아데노이드와 상기도 해부.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
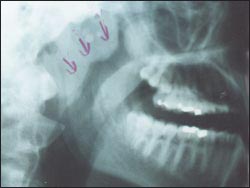
사진 152. 빨간색 화살표로 표시된 부위가 비대 된 아데노이드이다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
- 비강의 맨 후부, 인두 강의 맨 위 뒤 부위의 양쪽에 한 개씩 모두 두 개의 아데노이드가 정상적으로 있다.
- 아데노이드는 편도와 같이 림프절의 일종이다.
- 입을 크게 벌리고 목구멍(인두 강) 속을 육안으로 들여다봐도 아데노이드는 보이지 않는다. 그러나 특수 거울이 달린 의료기구로 목구멍 속을 육안으로 들여다보면 아데노이드가 보인다.
- 아데노이드 X-선 사진 검사나 초음파 검사, 또는 내시경 등으로 아데노이드가 비정상으로 큰지 정상 크기인지 정확히 알아볼 수 있다.
- 인두 강 맨 위 양 뒤쪽 부위에 있는 두 개의 아데노이드, 인두 강 후벽에 있는 인두 림프조직, 인두 강 좌우 양쪽에 있는 두개 편도, 혀뿌리 부위에 있는 한 개의 설편도가 있다. 아데노이드, 설편도, 인두 림프 조직, 편도 등이 둥근 가락지 모양으로 인두 강과 그 주위에 횡으로 배열되어 있다.
- 편도, 아데노이드 편도, 설편도 및 인두 림프 조직이 둥글게 감염병 방어 층을 횡으로 이루고 있다. 이런 방어층을 알다이어층 이라고 한다.
- 알다이어층은 비강이나 입을 통하여 호흡기 속으로, 또는 소화기 속으로 침입하는 병원체나 항원들이 신체의 다른 계통 기관이나 조직 속으로 더 이상 침입해 들어가지 못하게 하는 방어 역할을 한다.
- 즉 입이나 콧구멍을 통해 몸속으로 들어오는 병원체나 항원들이 인두 강 속 이상 호흡기 속, 소화관 속, 또는 그 외 신체 다른 계통의 기관 속으로 더 이상 침입하지 못하게 하는 방어 기능을 알다이어층이 한다.
- 아데노이드와 편도는 태어나서부터 12~13세까지 점점 더 커지다가 12~13세 이후부터는 더 이상 커지지 않고 그때 크기대로 있는 것이 보통이다. 편도비대 참조.
- 그렇지만 감기나 다른 종류의 바이러스 상기도 감염병을 앓을 때는 바이러스 감염으로 아데노이드와 편도가 더 커지고 더 붓는 것이 보통이다.
- 알레르기 비염, 아토피성 피부염, 기관지 천식 등 알레르기 질환이나 아토피성 체질이 있는 아이들의 아데노이드와 편도의 크기는 그렇지 않은 아이들에 비해 훨씬 더 큰 것이 보통이다.
- 아토피성 체질을 가진 아이들의 비강 점막층이 붓고 아데노이드도 붓고 후비강 기도 부분이 쉽게 막힐 수 있고 그 외 다른 이유로 잘 때 코를 골고 코로 숨쉬기가 곤란할 수 있다.
- 이런 문제가 있는 아이들은 거의 항상 입을 벌리고 숨 쉰다. 즉 경구호흡(구강호흡)을 하는 것이 보통이다. 이런 증상 징후가 몇 개월 내지 몇 년 동안 계속될 수 있다.
- 이 때 입, 이, 잇몸, 코, 입천장, 인두, 얼굴 등 해부적 구조와 상호 관계에 변화가 생겨 아데노이드형 얼굴(아데노이드 안모)이 생길 수 있다([부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다-소아가정간호백과]-제 15권 소아 청소년 알레르기 및 자가면역질환-알레르기 비염 참조).
Adenoids function and adenoidal hypertrophy

Figure 150. Upper and lower airways a-auricular, b-middle ear, c-ear canal, d-pharynx, e-larynx Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP Figure 151. Adenoid and upper airway anatomy. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Picture 152. The area indicated by the red arrow is an enlarged adenoid. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
• There are normally two adenoids, one on either side of the posterior part of the nasal cavity, the top posterior part of the pharyngeal cavity.
• Adenoids, like tonsils, are a type of lymph node.
• Even if you open your mouth wide and look into the throat (pharyngeal cavity) with the naked eye, you cannot see the adenoids. However, if you look into the throat with a medical device with a special mirror, you can see the adenoids.
• Adenoid X-ray examination, ultrasound examination, or endoscopy can accurately determine whether adenoids are abnormally large or normal in size.
• There are two adenoids in both posterior regions of the pharyngeal cavity, pharyngeal lymphoid tissue in the posterior wall of the pharyngeal cavity, two tonsils on either side of the pharyngeal cavity, and one lingual tonsil in the root of the tongue. Adenoids, lingual tonsils, pharyngeal lymphoid tissue, tonsils, etc. are arranged horizontally in and around the pharyngeal cavity in a round ring shape.
• Tonsils, adenoid tonsils, lingual tonsils, and pharyngeal lymphoid tissues form a circular, transverse infectious disease defense layer. This layer of defense is called the Aldyre layer.
• The Alder layer acts as a defense that prevents pathogens or antigens from entering the respiratory tract or digestive tract through the nasal passages or mouth from further invading into other organs or tissues of the body.
• In other words, the Alder layer has a protective function that prevents pathogens or antigens entering the body through the mouth or nostrils from entering the pharynx, the respiratory tract, the digestive tract, or other organs of the body
. • Adenoids and tonsils get bigger from birth to age 12 to 13, and after age 12 to 13, they don’t get bigger and usually remain the same size. See tonsil hypertrophy.
• However, when you have a cold or another type of viral upper respiratory tract infection, it is common for the adenoids and tonsils to become larger and more swollen due to a viral infection.
• Children with allergic diseases such as allergic rhinitis, atopic dermatitis, and bronchial asthma or with atopic constitution usually have much larger adenoids and tonsils than those without.
• Children with atopic constitution may have swelling of the nasal mucosa, swelling of adenoids, posterior nasal airway blockage, and difficulty snoring and snoring while sleeping for other reasons.
• Children with this problem almost always breathe with their mouths open. In other words, oral breathing (oral breathing) is normal. These symptoms may persist for months to years.
• At this time, anatomical structures such as mouth, teeth, gums, nose, the roof of the mouth, pharynx, face, etc. may change and adenoid face (adenoid face) may occur. Encyclopedia]-Vol. 15 Children and Adolescent Allergy and Autoimmune Diseases-Allergic Rhinitis).
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy of Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제1권 소아청소년 응급 의료
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제2권 소아청소년 예방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제3권 소아청소년 성장 발육 육아
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제4권 모유,모유수유, 이유
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유식, 비타민, 미네랄, 단백질, 탄수화물, 지방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제16권. 소아청소년 정형외과 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제17권. 소아청소년 피부 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제18권. 소아청소년 이비인후(귀 코 인두 후두) 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제19권. 소아청소년 안과 (눈)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제20권 소아청소년 이 (치아)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제21권 소아청소년 가정 학교 간호
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제22권 아들 딸 이렇게 사랑해 키우세요
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제23권 사춘기 아이들의 성장 발육 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제24권 소아청소년 성교육
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제25권 임신, 분만, 출산, 신생아 돌보기
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th- 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
- 응급환자관리 정담미디어
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- 소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
- The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
- Neonatology Jeffrey J. Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
- Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- 임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
- Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
- Sources and references on Growth, Development, Cares, and Diseases of Newborn Infants
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
- Emergency care, Harvey Grant and Robert Murray
- Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
- Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
- Neonatal resuscitation Ameican academy of pediatrics
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A.
- 제4권 모유, 모유수유, 이유 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유, 비타민, 단백질, 지방 탄수 화물 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제6권 신생아 성장발육 양호 질병 참조문헌 및 출처
- 소아과학 대한교과서
-
제18권 소아청소년 이비인후과 질환 참조문헌 및 출처
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Gray’s Anatomy
-
Habilitation of The handicapped Child, The Pediatric Clinics of North America, Robert H Haslam, MD.,
-
Pediatric Otolaryngology Sylvan Stool
-
Hearing Loss In children, The Pediatric Clinics of North America Nancy Roizen,MD and Allan O Diefendorf, PhD
-
Recent Advances in Pediatric otolaryngology The Pediatric Clinics of North America
-
Pediatric Otolaryngology. The Pediatric Clinics of North America, David Tunkel, MD., Kenneth MD Grundfast, MD
Copyright ⓒ 2014 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
“Parental education is the best medicine.