양성 급성 현기증, Benign paroxysmal dizziness
다음 정보를 참조(Please visit the following article) www.drleepediatrics.com-제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 제 2부 신체각계통 별 응급의료 제17장: 소아청소년 이비인후 질환 응급의료 참조
Please visit www.drleepediatrics.com-Volume 1 Emergency Medical Care for Children and Adolescents Part 2 Emergency Medical Care for Each System-Chapter 17: Pediatrics Ear, Nose. Throat, larynx Disease Emergency Medical Reference.
- 뇌에 현저한 이상도 없고 신체 다른 부위에도 아무런 기질적 병이 없는데 현기증이 갑자기 생겼다가 후유증 없이 완전히 낫는 현기증을 양성 급성 현기증이라고 한다.
- 양성 급성 현기증은 어느 연령층에도 생길 수 있다.
- 그렇지만 1∼4세 사이 아이들에게 더 잘 생긴다.
- 원인은 확실히 모르지만 내이(內耳)에 있는 균형 중추 신경 이상으로 생길 수 있다.
- 미로 염(Labyrinthitis) 으로도 어지럼 병이 생길 수 있다.
양성 급성 현기증의 증상 징후
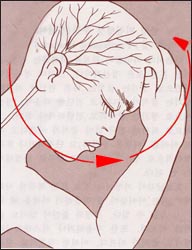
그림170. 현기증이 있으면 주위가 완아를 중심으로 해 빕빙 돌아가는 느낌이 생긴다..
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
- 정도에 따라 증상 징후가 차이가 있다.
- 양성 급성 현기증의 전형적 증상 징후는 다음과 같다.
- 지금까지 잘 놀던 아이에게 양성 급성 현기증이 갑자기 생기면, 갑자기 균형을 잃고 넘어지거나 주저앉는다.
- 때로는 갑자기 양성 급성 현기증이 일어날 때 당황해서 부모 앞으로 달려들기도 한다.
- 현기증이 다 없어질 때까지 가만히 눕든지, 부모를 붙들고 앉아 있을 수 있다.
- 말로 표현할 수 있는 유아에게 양성 급성 현기증이 일어나면 자기 주위에 있는 모든 것이 빙빙 돌아간다고 표현할 수 있다.
- 양성 급성 현기증은 의식을 잃지 않은 상태에서 3~4분 동안 지속되다가 자연히 없어지는 것이 보통이다.
- 현기증이 더 이상 발작되지 않으면 아무 일이 생기지 않은 듯이 일어나서 다시 놀거나 하던 일을 계속 진행할 수 있다.
- 양성 급성 현기증은 2∼3년 동안에 간간이 일어났다가 없어졌다가 하면서 재발될 수 있다.
- Labyrinthitis 으로 어즈럼 병이 생길 수 있다
양성 급성 현기증의 진단
- 병력·증상 징후·진찰소견 등을 종합하여 이 병을 진단할 수 있다.
- 현기증으로 생기는 증상 징후 이 외 별다른 이상은 없다.
- 중이, 내이 등을 진찰받고 필요에 따라 뇌파검사를 받고, 현기증이 다른 원인으로 생기는지 알아본다.
- 간질과 다른 종류의 발작성 질환과 양성 급성 현기증을 감별 진단해야 한다.
양성 급성 현기증의 치료
- 드라마민이나 meclizine 또는 그 외 다른 종류의 항히스타민제로 대증 치료할 수 있다.
- 시간이 지나가면 자연적으로 회복된다. 현기증(어지러움/Dizziness/Vertigo) 참조
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy of Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제1권 소아청소년 응급 의료
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제2권 소아청소년 예방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제3권 소아청소년 성장 발육 육아
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제4권 모유,모유수유, 이유
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유식, 비타민, 미네랄, 단백질, 탄수화물, 지방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제16권. 소아청소년 정형외과 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제17권. 소아청소년 피부 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제18권. 소아청소년 이비인후(귀 코 인두 후두) 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제19권. 소아청소년 안과 (눈)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제20권 소아청소년 이 (치아)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제21권 소아청소년 가정 학교 간호
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제22권 아들 딸 이렇게 사랑해 키우세요
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제23권 사춘기 아이들의 성장 발육 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제24권 소아청소년 성교육
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제25권 임신, 분만, 출산, 신생아 돌보기
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th- 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
- 응급환자관리 정담미디어
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- 소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
- The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
- Neonatology Jeffrey J. Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
- Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- 임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
- Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
- Sources and references on Growth, Development, Cares, and Diseases of Newborn Infants
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
- Emergency care, Harvey Grant and Robert Murray
- Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
- Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
- Neonatal resuscitation Ameican academy of pediatrics
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A.
- 제4권 모유, 모유수유, 이유 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유, 비타민, 단백질, 지방 탄수 화물 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제6권 신생아 성장발육 양호 질병 참조문헌 및 출처
- 소아과학 대한교과서
-
제18권 소아청소년 이비인후과 질환 참조문헌 및 출처
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Gray’s Anatomy
-
Habilitation of The handicapped Child, The Pediatric Clinics of North America, Robert H Haslam, MD.,
-
Pediatric Otolaryngology Sylvan Stool
-
Hearing Loss In children, The Pediatric Clinics of North America Nancy Roizen,MD and Allan O Diefendorf, PhD
-
Recent Advances in Pediatric otolaryngology The Pediatric Clinics of North America
-
Pediatric Otolaryngology. The Pediatric Clinics of North America, David Tunkel, MD., Kenneth MD Grundfast, MD
Copyright ⓒ 2014 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
“Parental education is the best medicine.
Benign paroxysmal dizziness
Please visit the following article www.drleepediatrics.com-Volume 1 Emergency medical care for children and adolescents Part 2 Emergency medical care for each body system Chapter 17: Emergency medical care for ENT diseases in children and adolescents
Please visit www.drleepediatrics.com-Volume 1 Emergency Medical Care for Children and Adolescents Part 2 Emergency Medical Care for Each System-Chapter 17: Pediatrics Ear, Nose. Throat, Larynx Disease Emergency Medical Reference.
Dizziness that occurs suddenly and completely resolves without any aftereffects when there is no significant abnormality in the brain or any organic disease in other parts of the body is called benign acute vertigo.
Benign acute vertigo can occur at any age.
Sometimes, labyrinthitis can cause dizziness.
However, it is more common in children between the ages of 1 and 4.
The cause is not known for sure, but it may be caused by abnormalities in the balance central nervous system in the inner ear.
Symptoms Signs of Benign Acute VertigoFigure 170. When you feel dizzy, you feel like everything around you is spinning around you.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
Symptoms and signs vary depending on the severity.
Typical symptomatic signs of benign acute vertigo include:
If a child who has been playing well until now suddenly develops benign acute vertigo, the child suddenly loses balance and falls or falls down.
Sometimes, when benign acute vertigo suddenly occurs, children panic and rush to their parents.
You can either lie still or sit while holding on to your parent until the dizziness goes away.
When an infant develops benign acute vertigo, which can be expressed verbally, it can be expressed as feeling that everything around them is spinning.
Benign acute vertigo usually lasts for 3 to 4 minutes without loss of consciousness and then disappears spontaneously.
Once you no longer experience dizziness, you can get up and go back to playing or continuing to do what you were doing as if nothing had happened.
Benign acute vertigo may occur and disappear intermittently over a period of 2 to 3 years and may recur.
Diagnosis of Benign Acute Vertigo
This disease can be diagnosed by combining the history, symptoms, signs, and examination findings.
There are no other abnormalities other than the symptoms and signs of dizziness.
Examine the middle ear, inner ear, etc., receive an electroencephalogram (EEG) test if necessary, and find out if vertigo is caused by other causes.
A differential diagnosis must be made between epilepsy and other types of paroxysmal disorders and benign acute vertigo.
Treatment of Benign Acute Vertigo
Symptomatic treatment can be achieved with Dramamine or meclizine and other types of antihistamines.
It will recover naturally over time. See Dizziness/Vertigo
Sources and references
NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22nd Ed
The Harriet Lane Handbook 22nd Ed
Growth and development of the children
Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy of Pediatrics
www.drleepediatrics.com Volume 1 Pediatric and Adolescent Emergency Medicine
www.drleepediatrics.com Volume 2 Prevention in Children and Adolescents
www.drleepediatrics.com Volume 3 Child and Adolescent Growth Development Parenting
www.drleepediatrics.com Volume 4 Breast milk, breastfeeding, weaning
www.drleepediatrics.com Volume 5 Artificial nutrition, milk, baby food, vitamins, minerals, proteins, carbohydrates, fats
www.drleepediatrics.com Volume 6 Newborn Growth Development Childcare Diseases
www.drleepediatrics.comVolume 7 Infectious Diseases in Children and Adolescents
www.drleepediatrics.comVolume 8 Respiratory Diseases in Children and Adolescents
www.drleepediatrics.comVolume 9 Digestive Diseases in Children and Adolescents
www.drleepediatrics.comVolume 10. Children and adolescents kidney and urogenital diseases
www.drleepediatrics.comVolume 11. Cardiovascular diseases in children and adolescents
www.drleepediatrics.comVolume 12. Neuropsychiatric disorders in children and adolescents, behavioral sleep problems
www.drleepediatrics.comVolume 13. Blood, lymph, and tumor diseases in children and adolescents
www.drleepediatrics.comVolume 14. Pediatric and adolescent endocrinology, genetics, chromosomes, metabolism, rare diseases
www.drleepediatrics.comVolume 15. Allergies and autoimmune diseases in children and adolescents
www.drleepediatrics.comVolume 16. Orthopedic diseases in children and adolescents
www.drleepediatrics.comVolume 17. Pediatric and adolescent skin diseases
www.drleepediatrics.comVolume 18. Otolaryngology (ear, nose, pharynx, larynx) diseases in children and adolescents
www.drleepediatrics.comVolume 19. Ophthalmological (eye) diseases in children and adolescents
www.drleepediatrics.com Volume 20 Tooth diseases in children and adolescents
www.drleepediatrics.com Volume 21 Pediatric and Adolescent Home School Nursing
www.drleepediatrics.com Volume 22 Raise your son and daughter with love like this
www.drleepediatrics.com Volume 23 Growth and development diseases of adolescent children
www.drleepediatrics.com Volume 24 Sexual Education for Children and Adolescents
www.drleepediatrics.com Volume 25 Pregnancy, Labor, Birth, and Newborn Care
Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th- 21st Edition
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
Emergency patient management Jeongdam Media
Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
Pediatric Home Nursing Encyclopedia – Parents must also be anti-doctors, by Sangwon Lee
The pregnancy Bible. By Joan Stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
Neonatology Jeffrey J. Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
From pregnancy to caring for a newborn. Lee Sang-won
Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
Sources and references on Growth, Development, Cares, and Diseases of Newborn Infants
Emergency Medical Services for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
Emergency care, Harvey Grant and Robert Murray
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
Neonatal resuscitation Ameican academy of pediatrics
Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A.
Volume 4 Breast Milk, Breastfeeding, Weaning References and Sources
Volume 5 Artificial nutrition, milk, weaning, vitamins, proteins, fats and carbohydrates References and sources
Volume 6: Good growth and development of newborns Diseases References and sources
Pediatrics Korean textbook
Volume 18 ENT diseases in children and adolescents References and sources
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
Gray’s Anatomy
Habilitation of The Handicapped Child, The Pediatric Clinics of North America, Robert H Haslam, MD.,
Pediatric Otolaryngology Sylvan Stool
Hearing Loss In children, The Pediatric Clinics of North America Nancy Roizen, MD and Allan O Diefendorf, PhD
Recent Advances in Pediatric otolaryngology The Pediatric Clinics of North America
Pediatric Otolaryngology. The Pediatric Clinics of North America, David Tunkel, MD., Kenneth MD Grundfast, MD